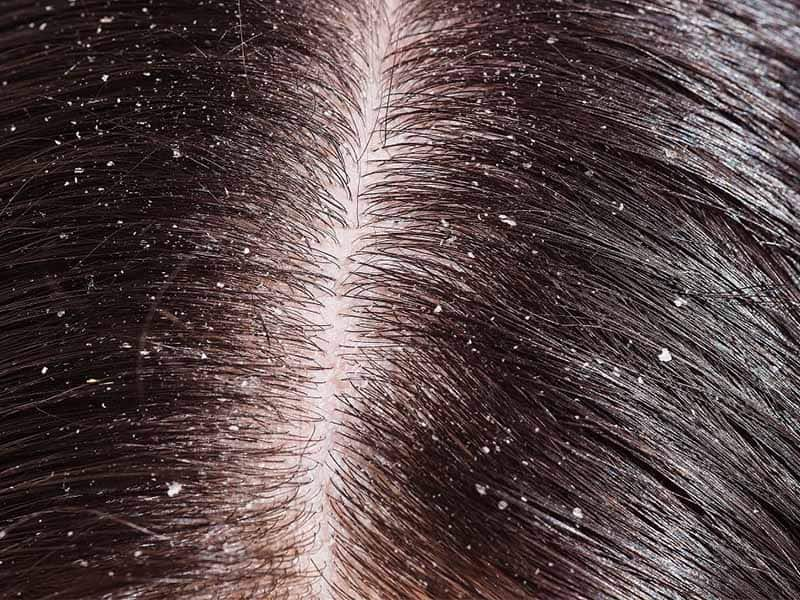
Dandruff is characterized by the shedding of small, dry bits of skin from the scalp, which can result in flakes in the hair and on the shoulders. It is also often accompanied by itching. While it is a widespread issue, the causes of dandruff are multifaceted and can include excess sebum production, the presence of fungi, and dry skin.
Dandruff may also be mistaken for other conditions such as dermatitis, which is characterized by inflammation, redness, and irritation, or psoriasis, which is a chronic skin condition marked by red, inflamed patches covered with silver-white scales. In this article, we will explore the different types of dandruff, their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and methods for prevention.
What is Dandruff?
Dandruff is a common skin condition characterized by dry, white flakes caused by a buildup of skin cells. It is not related to the condition of your hair or how frequently you wash it. The cause of dandruff is actually related to the condition of the skin on your scalp.

The issue is that skin cells grow and die far too quickly. The cause of this is unknown; however, one theory suggests that the common fungus Malassezia may play a role in dandruff. Most healthy adults have this fungus on their scalps and have no problems with it; however, some immune systems may overreact to it.
Stress or illness can make your dandruff worse. Cold, dry winters can aggravate existing dandruff or lead to its development.
Seborrheic dermatitis, or seborrhea, is a common cause of dandruff. Seborrheic dermatitis may also occur in other areas of the body, such as the ears, center of the face, and chest.
Causes of Dandruff
Numerous factors can contribute to dandruff, including:
Seborrheic dermatitis
A severe case of dandruff could actually be a mild case of seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic form of eczema that affects the areas of the body that secrete the most sebum, or oil.
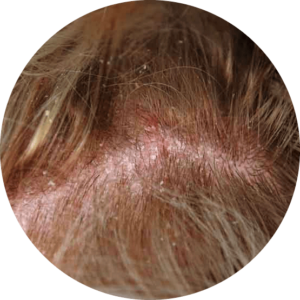
Oily skin is often associated with an increased risk of dandruff. The reason is a yeast called Malassezia globosa that feeds on the oils secreted by the sebaceous glands of the scalp. Some people’s bodies perceive this breakdown of oil as an irritant, causing the scalp to react by increasing the speed at which skin cells renew themselves and shed. In people without dandruff, it takes a whole month for new skin cells on the scalp to mature, die, and shed. However, in people with dandruff, this process takes only two to seven days.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis, also known as allergic contact dermatitis, is a skin reaction caused by an allergen or irritant that results in an itchy and possibly painful rash. The condition may be brought on by hair-care products or dyes. This can occur because of contact with the chemicals found in these products, according to the American Academy of Dermatology Association.
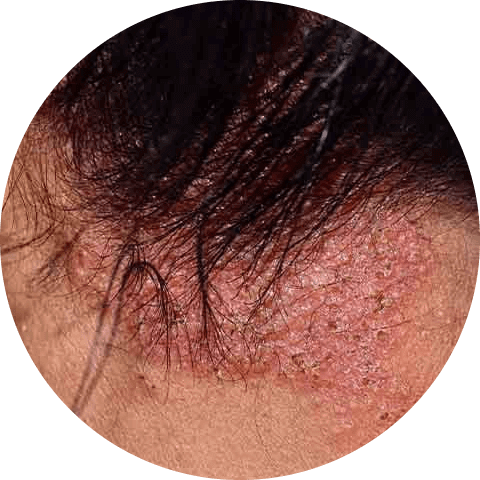
Dry skin
If the cold winter air dries out your skin all over, including your scalp, then dandruff may be caused by dry skin. Dandruff flakes tend to be smaller and less oily than seborrheic dermatitis flakes, both of which can be aggravated in climates with low humidity.
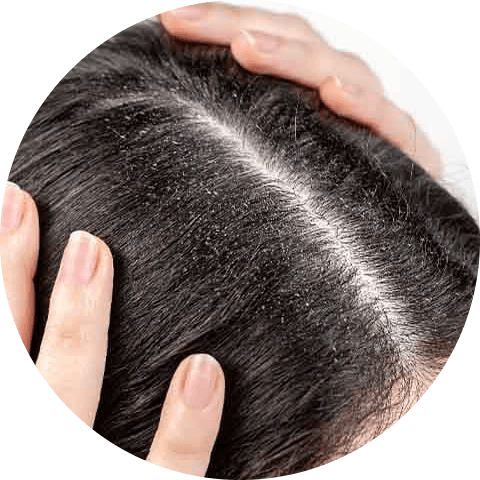

Risk Factors
Although almost anyone can get dandruff, the following factors may increase your risk:
Shampooing habits
For people who are already at risk for dandruff, washing infrequently can exacerbate the condition. On the other hand, taking extended breaks from washing can lead to oil buildup that can cause an individual to develop dandruff.
Age
Dandruff usually begins in young adulthood and lasts through midlife. This does not mean that older people are never affected. For some people, dandruff is a lifelong problem.
Sex
Androgen hormones like testosterone stimulate sebaceous gland activity and sebum production. More sebum increases the likelihood of an inflammatory reaction and dandruff. Men are more likely than women to develop dandruff.
Weakened immune system
Seborrheic dermatitis (a.k.a. dandruff) is more common in people who have had an organ transplant or HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, or alcoholic pancreatitis.
Neurologic and psychiatric conditions
Dandruff can be exacerbated by certain conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, and spinal cord injury.
Oily skin
People with naturally oily skin are more likely to develop seborrheic dermatitis.
Types of Dandruff
There are different types of dandruff, each with a specific cause. Some types can be treated by adjusting your hair care routine or using home remedies. However, other types may require prescription medications.
Dandruff on dry skin
Dry skin dandruff is a common type of dandruff that can occur during the winter months due to cold weather and indoor heating, as well as regular washing of the hair with hot water.
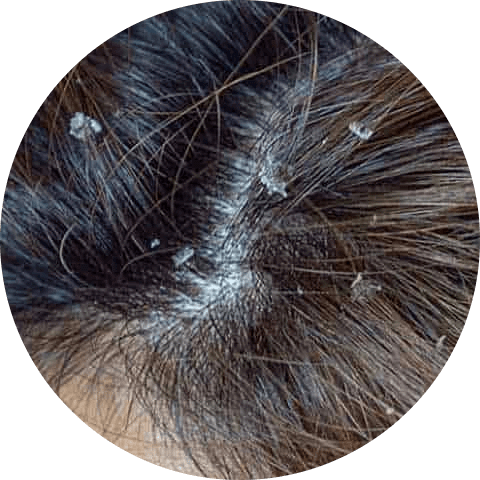

This type of dandruff is characterized by small, white flakes of dry skin on the scalp that may be accompanied by mild itching. If the itching becomes severe, it may be a sign of a more serious skin condition that requires medical attention.
To prevent dry skin dandruff, you can use a moisturizing shampoo and try home remedies like a coconut oil scalp massage to keep your scalp hydrated and reduce itching.
Dandruff on greasy skin
Oily skin dandruff is caused by an excess of sebum produced by the sebaceous glands just below the surface of the skin. This excess oil can irritate the scalp and cause dandruff.
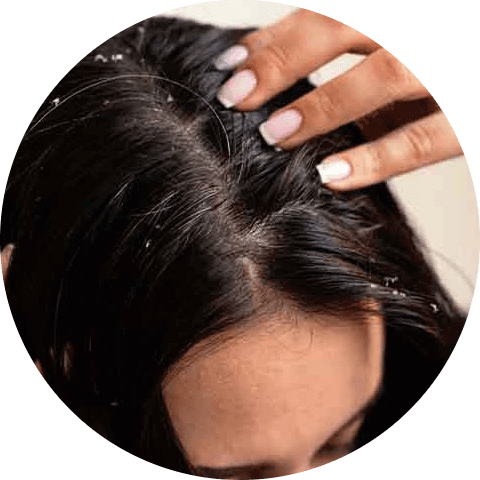

Oily skin dandruff tends to have larger flakes than dry skin dandruff, and these flakes may appear yellow and oily. Seborrheic dermatitis is a more severe form of dandruff that can occur on oily skin.
To treat oily skin dandruff, try shampooing on a regular basis and using a dandruff shampoo containing salicylic acid.
Dandruff caused by fungi
Dandruff and other skin conditions like eczema can be caused by an inflammatory response triggered by a type of fungus called Malassezia, which is found on the skin of all humans.
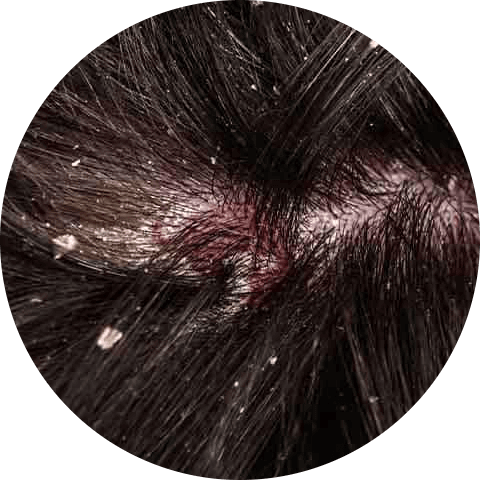

To treat fungus-related dandruff, you can use a shampoo with ingredients that inhibit Malassezia, such as zinc pyrithione. A 2018 study found that this type of shampoo may also be effective in preventing or treating other scalp conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, and eczema.
Additionally, applying diluted tea tree oil or using a shampoo with tea tree oil may help reduce fungus-related dandruff.
Psoriasis, eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis are a few common skin conditions that can affect your scalp and result in dandruff.
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that is characterized by flaky, itchy skin patches and, in some cases, a red rash. When this inflammatory condition affects the scalp, it can cause larger than normal flakes and red, irritated skin.
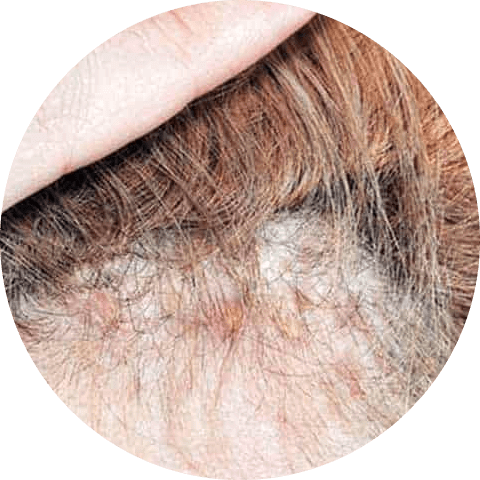
To help manage eczema on the scalp, it may be helpful to use a gentle, moisturizing shampoo. In more severe cases, a stronger topical treatment prescribed by a dermatologist may be necessary.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Oily skin is a risk factor for the development of seborrheic dermatitis, which is a severe form of dandruff. This common scalp condition can cause symptoms such as itching, redness, scaly patches, and flaky skin in addition to dandruff.
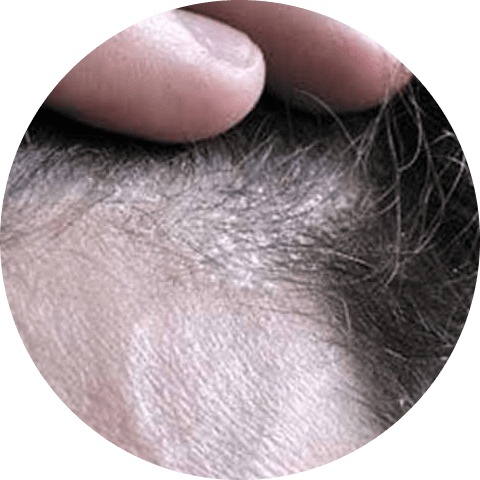
To effectively treat dandruff related to seborrheic dermatitis, it is recommended to use a shampoo containing zinc pyrithione.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that is believed to be caused by an autoimmune disorder. In people with psoriasis, skin cells grow at an accelerated rate, leading to the development of thick, scaly patches on the skin. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, around half of all individuals with psoriasis also experience scalp psoriasis.
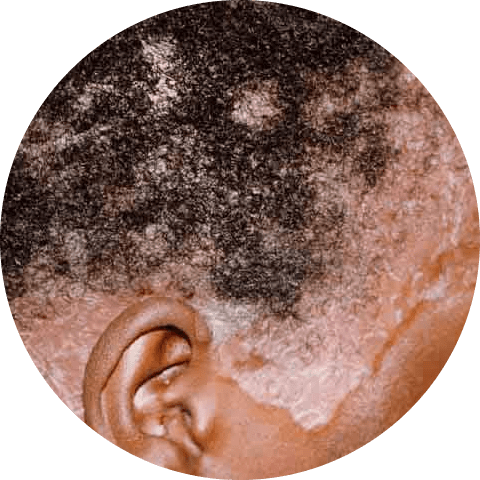
Psoriasis of the scalp can present as fine, powdery flakes with a silver sheen or as raised, inflamed, scaly patches of skin covered in a silvery-white buildup of dead skin cells.
To manage flare-ups of scalp psoriasis, corticosteroids may be used. Additionally, shampoos containing salicylic acid or zinc pyrithione may help to alleviate the symptoms of scalp psoriasis.
Symptoms of Dandruff
Dandruff is a common condition that causes the skin on your scalp to flake and peel. It’s usually harmless and easy to treat, but it can be persistent and frustrating. In addition to the flaky skin and itchy, scaly scalp, dandruff can also cause other symptoms such as red patches on the scalp, eyebrow dandruff, and even hair loss.
These symptoms are often more noticeable in the fall and winter months when the air is dry. Dandruff can also cause dry skin flakes to appear on the face, which can be embarrassing and difficult to cover up. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dermatologist or healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
You can get more information about online dermatology consultation by click on the link.
Dandruff vs Dry Scalp
Dandruff and dry scalp are two common scalp conditions that can cause flakes and itching. While they may seem similar, there are some key differences between dandruff and dry scalp.
Dandruff is a scalp condition that is characterized by the presence of white flakes on the scalp and hair. It is often caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the scalp, which can lead to excessive shedding of skin cells. Dandruff can also be triggered by factors such as stress, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
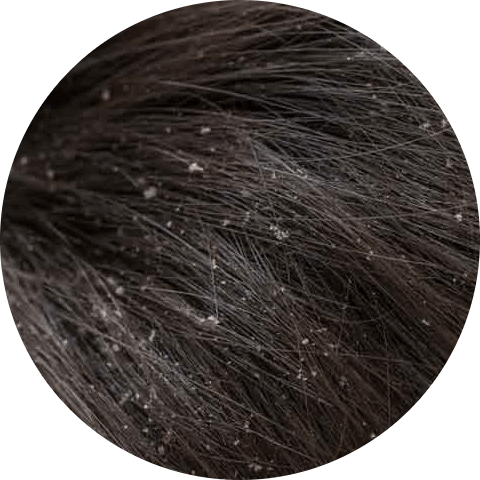

Dry scalp, on the other hand, is a condition in which the scalp lacks sufficient moisture. This can lead to the shedding of dry, flaky skin cells and can cause the scalp to feel itchy and uncomfortable. Dry scalp can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to harsh weather, using harsh hair care products, and having a naturally dry scalp.
To determine whether you have dandruff or dry scalp, it is important to pay attention to the appearance of the flakes and any other symptoms that you may be experiencing. Dandruff flakes are typically larger and more yellowish in color, while dry scalp flakes are smaller and more white. If you are unsure about the cause of your flakes, it is a good idea to speak with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Dandruff vs. Eczema
Dandruff and eczema are two common skin conditions that can cause itching, flaking, and redness of the skin. While they may share some similar symptoms, they are actually quite different conditions with different causes and treatment approaches.
Dandruff is a common condition that causes the skin on the scalp to flake and peel. It is often caused by a yeast-like fungus called malassezia, which lives on the scalp and feeds on the natural oils produced by the skin. Dandruff can also be caused by dry skin, sensitivity to certain hair care products, and certain medical conditions. Treatment for dandruff usually involves the use of over-the-counter or prescription shampoos and other scalp treatments.
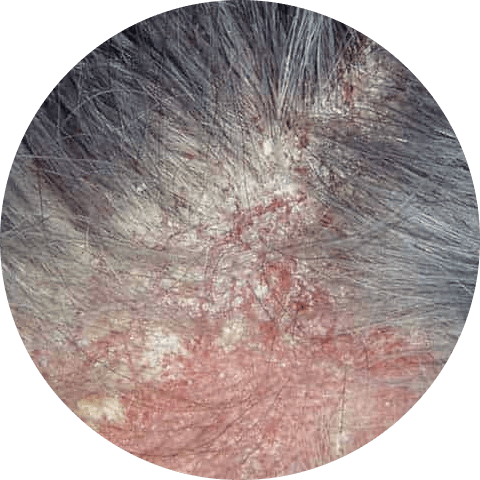
Eczema, on the other hand, is a chronic skin condition that causes the skin to become inflamed, red, and itchy. It can affect any part of the body, but is most commonly found on the face, hands, and legs. Eczema is often inherited and can be triggered by various factors such as allergies, stress, and environmental irritants. Treatment for eczema involves identifying and avoiding triggers, using moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated, and taking medications to reduce inflammation and itching.
While dandruff and eczema may have some similar symptoms, they are two distinct skin conditions that require different treatment approaches. It’s important to see a dermatologist or healthcare provider to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Dandruff Treatment
Dandruff is a common and often chronic condition that can be treated with various methods. The first step in treating dandruff is to use a gentle over-the-counter (OTC) shampoo to wash the hair daily. This will help reduce oil and skin cell buildup on the scalp. If a gentle shampoo is not effective, you can try an OTC dandruff shampoo. It is recommended to alternate between two or three different dandruff shampoos to find the one that works best for you. Some common active ingredients in dandruff shampoos include selenium sulfide, pyrithione zinc, salicylic acid, ketoconazole, and tar.
If OTC shampoos do not improve your dandruff, your dermatologist may prescribe a prescription-strength antifungal shampoo or a topical corticosteroid lotion. An alternative to corticosteroids is a class of drugs called calcineurin inhibitors, which work by suppressing the immune response.

In addition to traditional treatment methods, some people find relief from dandruff by using shampoos or topicals with tea tree oil, increasing their intake of omega-3 fatty acids, and getting brief bouts of sunshine. However, if you are using a tar-based dandruff treatment, it is important to avoid direct sun exposure, as the scalp can be sensitive to sunlight. It is also a good idea to cut back on hair products that can build up on the scalp and contribute to dandruff.
It is also important to practice good scalp hygiene when treating dandruff. This includes avoiding excessively scratching the scalp, as this can further irritate the skin and make dandruff worse. It is also important to avoid sharing hats, combs, and other hair accessories with others, as dandruff is contagious and can spread easily.
Additionally, consider making lifestyle changes that may help improve your dandruff. This can include reducing stress, eating a healthy diet that is rich in nutrients, and getting enough sleep. These changes can help improve overall skin health and may help reduce the frequency and severity of dandruff.
If you have tried various dandruff treatments and are still experiencing symptoms, it may be necessary to see a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment. They will be able to assess your individual situation and recommend the most appropriate course of treatment for your specific needs. It is possible to effectively manage and reduce dandruff symptoms with the right treatment and self-care measures.
For those seeking relief from persistent dandruff issues that don’t respond to over-the-counter treatments, consulting a dermatologist for dandruff treatment can be a valuable step. At RemoteDerm, our experienced dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and addressing various scalp conditions, including dandruff. Don’t let persistent dandruff affect your scalp health and confidence; take the first step towards effective dandruff treatment by getting an online consultation with our dedicated specialists in Canada.
Dandruff Prevention
Dandruff can be embarrassing and frustrating to deal with, but there are steps you can take to prevent dandruff from occurring or recurring.
One of the most effective ways to prevent dandruff is by keeping your scalp clean. This means washing your hair regularly with a gentle, anti-dandruff shampoo. Look for shampoos that contain ingredients like pyrithione zinc, selenium sulfide, or ketoconazole, as these have been shown to be effective at controlling dandruff. Be sure to follow the instructions on the shampoo bottle and only use it as directed. Overuse of dandruff shampoo can lead to dry, irritated skin.

Another important step in preventing dandruff is to avoid using styling products that can build up on the scalp. This includes hair gels, mousses, and hairsprays. These products can clog pores on the scalp, leading to an increase in dandruff. If you do use styling products, be sure to wash them out thoroughly to remove any build-up.
In addition to keeping your scalp clean, it’s also important to eat a healthy diet. A diet that is high in essential nutrients, such as vitamins A, B, and E, can help keep your scalp healthy and prevent dandruff. Foods like eggs, nuts, and leafy green vegetables are all rich in these nutrients.
Stress can also contribute to dandruff, so it’s important to try to manage stress levels. This can include practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, or finding ways to reduce the sources of stress in your life.
Another way to prevent dandruff is by avoiding harsh hair treatments like hot oil treatments or tight hairstyles that can irritate the scalp. If you have long hair, try to avoid brushing it back tightly, as this can put pressure on the scalp and lead to dandruff.
It’s also important to avoid sharing combs, brushes, and other hair care tools with others, as this can spread dandruff-causing fungi from one person to another. If you do share these items, be sure to clean them thoroughly before using them again.
If you’re prone to dandruff and have tried these prevention methods without success, it may be necessary to see a dermatologist. They can assess your scalp and recommend a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
Dandruff is a common scalp condition that is characterized by the presence of white flakes on the scalp and hair. While dandruff flakes may look similar, they can be caused by a variety of scalp conditions. To determine the cause of your dandruff, it is important to pay attention to the appearance of the flakes, the condition of your skin and hair, and any other symptoms that you may be experiencing.

There are several treatment options available for dandruff, including over-the-counter (OTC) antidandruff shampoos and changes to your hair care routine. In some cases, prescription shampoos may be necessary to effectively get rid of dandruff. If you think you may have dandruff, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Your doctor or dermatologist will be able to determine the type of dandruff you have and provide advice on the best course of action for treating it.
Dandruff FAQs
1. Is Dandruff contagious?
No, dandruff is not contagious. However, certain fungal infections that can cause dandruff can be spread through shared hair care tools or close contact with someone who has the infection.
2. Can Dandruff be cured?
Dandruff can usually be controlled with proper hair care and the use of anti-dandruff shampoos. In some cases, a dermatologist may be needed to determine the cause of the dandruff and recommend a specific treatment plan.
3. Can Dandruff lead to hair loss?
In some cases, severe dandruff can cause temporary hair loss due to the inflammation it can cause on the scalp. However, proper treatment of dandruff can usually prevent hair loss from occurring.
4. Can diet play a role in Dandruff?
A healthy diet that is rich in essential nutrients, such as vitamins A, B, and E, can help keep the scalp healthy and prevent dandruff. A diet high in processed foods and sugar may contribute to dandruff.
5. How often should I wash my hair if I have Dandruff?
It’s generally recommended to wash your hair every 2–3 days if you have dandruff. Using an anti-dandruff shampoo can help to control the condition and prevent it from recurring. However, it’s important not to overuse the shampoo, as this can lead to dry, irritated skin.

4 comments
What are some home remedies for dandruff? I’ve heard of using apple cider vinegar, is that true?
Hello Susan, There are several home remedies that people use to help manage dandruff, including apple cider vinegar. However, it’s important to keep in mind that what works for one person may not work for another. We always recommend speaking with a dermatologist to find the best treatment plan for you, as some remedies may actually make dandruff worse.
Hi I wanted to know can dandruff lead to other hair problems like hair loss?
Hi there! Actually dandruff itself does not directly lead to hair loss, but scratching a persistent, itchy scalp can cause temporary hair loss. It’s important to treat dandruff effectively to reduce itching and prevent hair loss.