Phymatous Rosacea, a lesser-known but significant subtype of Rosacea, can affect the skin’s texture and appearance, leading to discomfort and self-esteem issues. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for Phymatous Rosacea, shedding light on this skin condition that affects many individuals.
Before diving into Phymatous Rosacea’s specifics, let’s establish a basic understanding of Rosacea itself. Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. It often begins with episodes of flushing and blushing and can progress to more persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and the development of bumps and pimples, particularly in the central facial region. While Rosacea can affect anyone, it is most commonly seen in individuals with fair skin.
What is Phymatous Rosacea?
Phymatous Rosacea is one of the subtypes of Rosacea, and it is characterized by thickened, bumpy skin with a pronounced texture. This subtype is typically associated with enlargement of the sebaceous (oil) glands, causing the skin to appear swollen and irregular. The most common areas affected by Phymatous Rosacea include the nose, chin, and forehead.
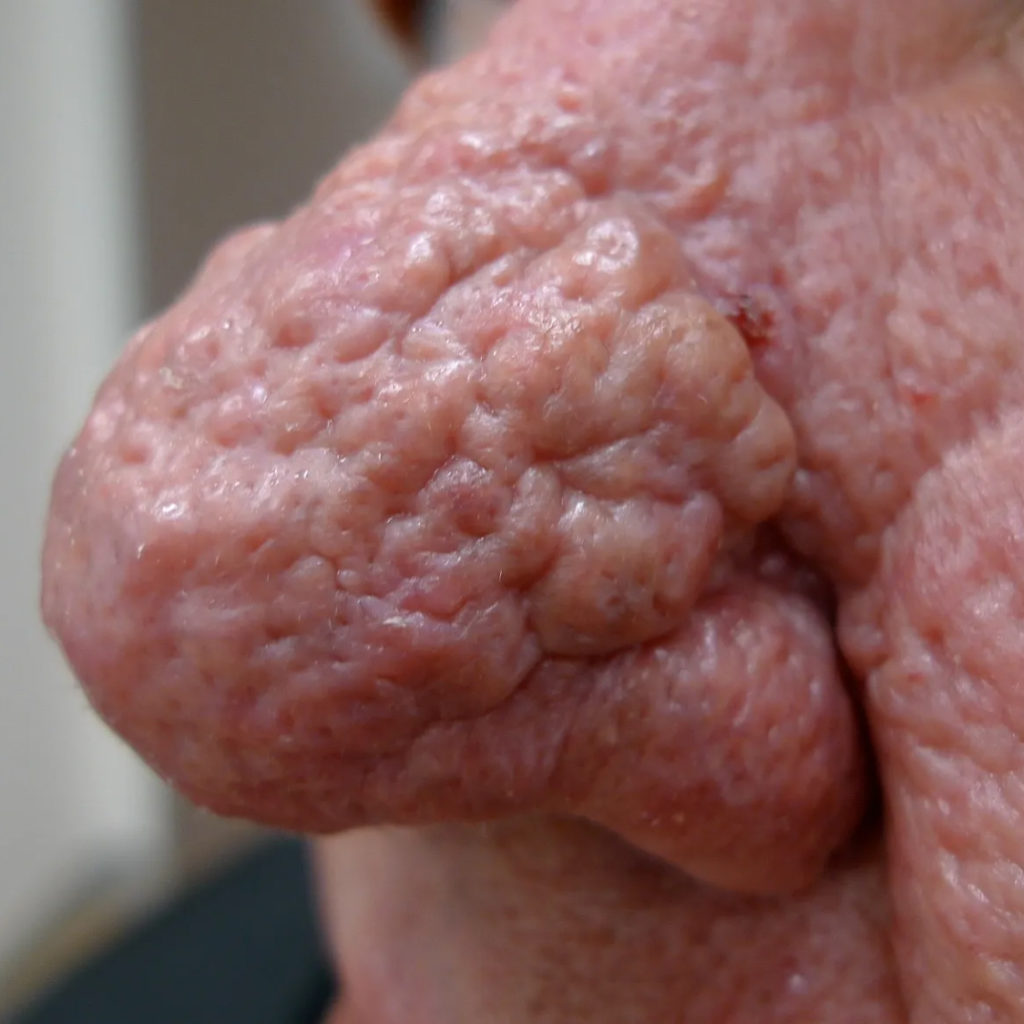
Causes of Phymatous Rosacea
The exact cause of Phymatous Rosacea is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent and protracted inflammation within the facial skin is a hallmark of Rosacea in general. In the context of Phymatous Rosacea, this ongoing inflammatory process assumes paramount importance. It fuels the collagen overproduction, ultimately leading to skin thickening and enlargement.
- Genetic Predisposition: Emerging evidence suggests a hereditary component in the predisposition to Rosacea, which encompasses the various subtypes, including Phymatous Rosacea. Genetic factors may influence one’s susceptibility to developing this condition, making certain individuals more prone to its manifestation.
- Demodex Mites: An intriguing facet of Rosacea is the presence of Demodex mites, minuscule arachnids that naturally reside on human skin. Interestingly, individuals with Rosacea, including those with Phymatous Rosacea, tend to harbour higher populations of these microscopic creatures. This prevalence of Demodex mites is thought to be linked to the perpetuation of inflammation in affected individuals, potentially exacerbating the condition.
Symptoms of Phymatous Rosacea
Recognizing the symptoms of Phymatous Rosacea is essential for early diagnosis and intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Thickened Skin: The skin may become thick, rough, and bumpy, particularly on the nose, leading to a condition commonly referred to as “rhinophyma.”
- Enlarged Pores: The sebaceous glands may enlarge, causing the pores to become more prominent.
- Nasal Deformity: In severe cases, Phymatous Rosacea can lead to nasal deformity, altering the shape of the nose.
- Oily Skin: Increased oil production can contribute to the development of pimples and acne-like lesions.
Phymatous Rosacea Treatment Options
The management of Phymatous Rosacea offers a range of therapeutic avenues, providing individuals with several effective options to address this skin condition comprehensively:
- Topical Medications: Dermatologists employ a variety of topical formulations, such as creams or gels, often containing antibiotics, retinoids, or other pharmacological agents. These topicals are meticulously selected to mitigate inflammation, alleviate redness, and enhance the overall texture of the affected skin. They serve as a first-line intervention in many cases, offering a non-invasive approach to symptom control.

- Oral Medications: In instances where the condition’s severity necessitates a more systemic approach, oral medications come into play. Antibiotics like doxycycline or isotretinoin may be prescribed, targeting inflammation from the inside out. By reducing the inflammatory response internally, these medications can be instrumental in managing the progression of Phymatous Rosacea.
- Laser Therapy: Cutting-edge laser treatments have emerged as a transformative option for Phymatous Rosacea. These advanced procedures are adept at homing in on visible blood vessels, diffusing redness, and addressing the thickened skin characteristic of this condition. The result is a noticeable enhancement in skin texture and an overall restoration of a smoother complexion.
- Surgery: In cases where Phymatous Rosacea has advanced significantly, particularly leading to the development of rhinophyma, surgical intervention may be warranted. Surgical procedures are tailored to reshape and restore the affected areas, not only alleviating cosmetic concerns but also enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
- Skincare Regimen: A pivotal aspect of Phymatous Rosacea management is the cultivation of a personalized skincare routine. This tailored regimen typically involves the selection of gentle cleansers, hydrating moisturizers, and broad-spectrum sunscreens. These measures are designed not only to manage existing symptoms but also to prevent the onset of flare-ups, fostering long-term skin health.
The comprehensive range of treatment modalities available for Phymatous roacea, including online rosacea treatment options, underscores the importance of consulting with a dermatologist to devise an individualized plan that best addresses the specific needs and severity of this condition in each patient. By leveraging these diverse therapeutic approaches, individuals can regain confidence in their skin’s appearance and overall well-being.
How to Treat Phymatous Rosacea at Home
Efficiently managing Phymatous Rosacea requires the expert guidance of a healthcare professional. Nonetheless, there are valuable self-care practices you can integrate into your daily routine to complement your treatment plan and foster an environment of skin wellness. Here are several at-home strategies to consider:
- Gentle Cleansing: Incorporate a gentle, non-abrasive cleanser into your daily skincare regimen. Wash your face twice a day using lukewarm water to remove impurities and excess oil without causing irritation. Avoid vigorous scrubbing, as this can exacerbate the redness and inflammation associated with Phymatous Rosacea.
- Sun Protection: One of the most crucial aspects of managing Phymatous Rosacea is safeguarding your skin from harmful UV rays. Prior to venturing outdoors, apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30. This proactive measure shields your skin from the sun’s damaging effects, which can trigger and worsen symptoms of Rosacea.

- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that can aggravate your Phymatous Rosacea symptoms is critical. Spicy foods, alcohol consumption, and exposure to extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) are all common triggers. You can significantly reduce the likelihood of flare-ups and discomfort by recognizing these factors and making conscious efforts to avoid them.
- Hydrate and Moisturize: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your skin properly hydrated. Apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to your skin on a regular basis to help it maintain its natural barrier function. Skin that is well-hydrated is less prone to irritation and redness.
- Stress Management: Rosacea symptoms are known to be exacerbated by stress. To help manage stress, try stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga. A calm and relaxed mind can benefit your skin’s overall health.
- Avoid Harsh Skincare Products: Avoid skincare products containing harsh ingredients, fragrances, or alcohol, as these can be irritating to Rosacea-prone skin. Choose products that are labeled “hypoallergenic” or “suitable for sensitive skin.”
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Keep a symptom diary to keep track of your daily activities, diet, and skincare routine. This can assist you in identifying patterns and potential triggers that contribute to your Phymatous Rosacea symptoms, allowing you to make educated changes.
Final Thoughts
Phymatous Rosacea, a subtype of Rosacea, can significantly impact one’s well-being. While its exact causes remain unclear, a range of treatment options is available, including medical interventions like topical and oral medications, laser therapy, and surgery. Collaborating with a dermatologist for personalized treatment plans is crucial, as they can tailor approaches to individual needs and severity.
Simultaneously, self-care practices detailed in this guide empower individuals to actively manage their condition. By incorporating gentle cleansing, sun protection, trigger avoidance, and a thoughtful skincare routine, individuals can reduce the frequency and intensity of flare-ups. Maintaining skin hydration, practising stress management, and making informed choices about skincare products all contribute to overall skin health.
FAQs
- Is Phymatous Rosacea hereditary?
There’s evidence suggesting a genetic component in the predisposition to Rosacea, including Phymatous Rosacea.
- Can individuals with Phymatous Rosacea drink alcohol?
Alcohol consumption can be a trigger for some individuals, so it’s advisable to monitor its effects on symptoms.
- Can Phymatous Rosacea be cured completely?
While it can be managed effectively, a complete cure may not always be possible, but ongoing treatment and self-care can help control the condition and its symptoms for improved quality of life.
- Can Phymatous Rosacea affect people with darker skin tones?
Yes, while more common in fair-skinned individuals, Phymatous Rosacea can affect people with darker skin tones as well.
