Female pattern alopecia (FPA), also known as female pattern baldness, is a condition that affects millions of women worldwide and affects their self-esteem. While it can be distressing, there are effective treatments available to slow down or stop hair loss and promote regrowth. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for FPA.
Causes of Female Pattern Alopecia
The exact female pattern baldness causes are not fully understood, but research suggests that it is a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. If you need to consult with an online dermatologist, you can use Remotederm services.

Genetics
One of the female pattern baldness causes is genetics. If you have a family history of hair loss or baldness, you are more likely to develop FPA yourself. Researchers have identified several genes that play a role in hair growth and loss, including the AR gene and the PAX1 gene. These genes can affect the sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens, which are male hormones that can contribute to hair loss.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones can also play a significant role in FPA. Androgens, such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are male hormones that both men and women produce. In women, androgens are typically produced in small amounts by the ovaries and adrenal glands. However, if the body produces too much androgen, it can lead to Androgenic alopecia. click to read more about Androgenic alopecia.
Androgens can cause hair follicles to shrink and shorten the lifespan of hair strands. Over time, this can lead to thinner, shorter hair and eventually to hair loss. Women who experience hormonal imbalances due to pregnancy, menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or certain medications may be at a higher risk of developing FPA.
Other Factors
In addition to genetics and hormonal imbalances, there are other factors that may contribute to FPA. These include:
- Age: Hair naturally becomes thinner and more brittle as we age, which can make it more prone to breakage and hair loss.
- Nutritional deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamin D, can contribute to hair loss.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the normal growth cycle of hair follicles and lead to hair loss.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, blood thinners, and antidepressants, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
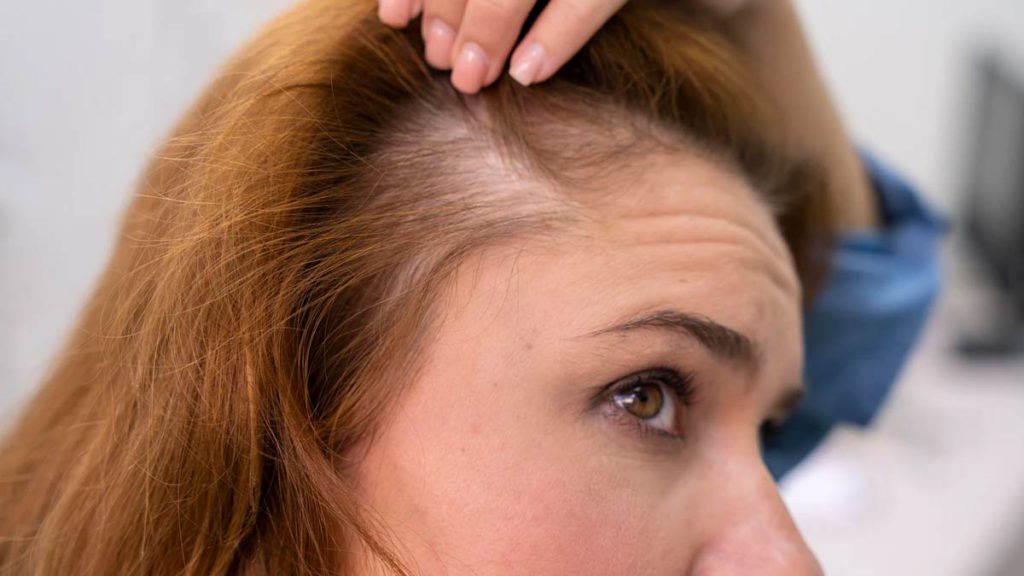

Symptoms of Female Pattern Alopecia
The female pattern baldness symptoms are characterized by gradual hair thinning and loss, which can occur anywhere on the head. Here are some of the most common female pattern baldness symptoms:
Gradual Hair Thinning
The most common symptom of FPA is gradual hair thinning. This typically occurs on the top and front of the scalp, but it can also occur elsewhere on the head. The hair may become thinner and shorter over time, and you may notice that it’s more difficult to style or manage. You may also notice more hair falling out when you brush or wash your hair.
Widening Part Line
As the hair on the top of the scalp thins, you may notice that your part line is widening. This can make your scalp more visible through your hair and create the appearance of bald spots or patches.
Receding Hairline
In some cases, FPA can cause a receding hairline. This typically occurs at the temples and forehead, and it can be more pronounced in some women than others. A receding hairline can make it more difficult to style your hair and can be a source of embarrassment or self-consciousness.
Sparse Hair at Temples and Forehead
As the hair on the top of the scalp thins, you may also notice that the hair around your temples and forehead becomes sparse. This can create a “V” shape in the front of your hairline and make it more difficult to style your hair.
Overall Hair Volume Decrease
Over time, FPA can lead to an overall decrease in hair volume. This can make your hair look flat, limp, or lifeless, and it can be especially noticeable in certain hairstyles or lighting conditions.
Diagnosing Female Pattern Alopecia
If you are experiencing hair loss or thinning, it’s important to see a healthcare provider or dermatologist who can help diagnose your condition. Your doctor will begin by conducting a physical exam of your scalp and hair and may ask about your medical history and any medications you are taking. They may also perform blood tests to check for underlying medical conditions that can contribute to hair loss. To read more about hair loss, its causes, and treatment options, click on this article.
In some cases, your doctor may also perform a scalp biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of skin from your scalp to examine under a microscope. This can help rule out other potential causes of hair loss, such as infections or autoimmune disorders.
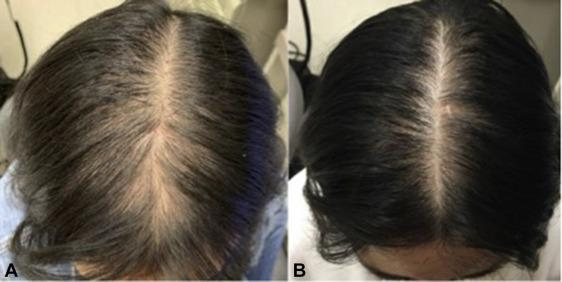
Treatment Options for Female Pattern Alopecia
While there is no cure for female pattern alopecia, there are several treatments available to slow down or stop hair loss and promote regrowth. The most common treatments include:
- Topical Minoxidil: A medication applied to the scalp to stimulate hair growth. Minoxidil is available over the counter in strengths ranging from 2% to 5%, and it has been shown to be effective as a female pattern baldness treatment. It works by widening blood vessels in the scalp, allowing more oxygen and nutrients to reach the hair follicles.
- Oral Finasteride: A medication that blocks the production of androgens and promotes hair growth. Finasteride is available by prescription only, and it is typically used to treat male pattern baldness. However, studies have shown that it can also be effective at treating FPA in some women.
- Oral Minoxidil: patients who are not able to tolerate topical minoxidil may be a good candidate for oral one. The medication can provide considerable improvement for androgenic alopecia but has its own potential side effects. Your dermatologist can discuss this medication in detail with you.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive female pattern baldness treatment that uses red light to stimulate hair follicles. LLLT devices emit low-level wavelengths of light that can penetrate the scalp and stimulate hair growth. While the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, studies have shown that LLLT can be effective at slowing down hair loss and promoting regrowth.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: A procedure that involves harvesting healthy hair follicles from one part of the scalp and transplanting them to areas of thinning or baldness. Hair transplant surgery is typically reserved for women who have significant hair loss and who have not responded to other treatments.
In addition to these treatments, some women may also consider using hair pieces or wigs to conceal their hair loss. These can be especially helpful for women who experience significant emotional distress due to FPA. If you have any questions regarding female pattern baldness, you can use an online dermatology consultation service, like Remotederm.

Preventing Female Pattern Alopecia
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent female pattern alopecia, there are steps you can take to minimize your risk of hair loss. Here are some tips for maintaining healthy hair and reducing your risk of FPA:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals, such as protein, iron, zinc, vitamin D, and biotin, can help promote healthy hair growth.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss by disrupting the normal growth cycle of hair follicles. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through meditation, yoga, or exercise, can help reduce your risk of FPA.
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Wearing tight hairstyles that pull on the hair, such as braids or ponytails, can cause damage to the hair follicles and lead to hair loss. Opt for looser hairstyles, and avoid wearing your hair in the same style every day.
- Protect Your Hair from Heat Damage: Overuse of heat styling tools, such as blow dryers, curling irons, and straighteners, can cause damage to the hair shaft and lead to hair loss. Use these tools sparingly, and always protect your hair with a heat-protectant spray.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking has been linked to hair loss in both men and women. If you smoke, quitting can help reduce your risk of developing FPA.

Coping with Female Pattern Alopecia
Dealing with hair loss can be challenging, but there are strategies you can use to cope with the emotional impact of FPA. Here are some tips for coping with FPA:
- Talk to a Therapist or Support Group: Talking to a therapist or joining a support group can help you process your feelings about hair loss and develop coping strategies.
- Experiment with Fashion and Makeup: Trying out new fashion and makeup styles can help you feel more confident and comfortable with your appearance.
- Practice Self-Care: Taking care of yourself, both physically and emotionally, can help reduce stress and improve your overall well-being. This may include activities such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones.
- Consider Hair Pieces or Wigs: Hairpieces or wigs can be a helpful way to conceal hair loss and boost your self-confidence.
- Accept Your Hair Loss: Accepting your hair loss and embracing new hairstyles or head coverings can help you feel more comfortable and confident in your appearance.

Conclusion
Female pattern alopecia is a common condition that affects many women. If you’re experiencing symptoms of FPA, it’s important to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and discuss your treatment options.
While there is no cure for FPA, there are effective treatments available to slow down or stop hair loss and promote regrowth. By taking steps to care for your hair and overall health, you can help minimize your risk of developing FPA and maintain healthy, voluminous hair throughout your life.
FAQs
- What causes female pattern baldness?
Female pattern baldness is caused by genetic factors and hormonal changes, specifically an increased sensitivity to androgens (male hormones) in the hair follicles.
- Is female pattern baldness hereditary?
Yes, female pattern baldness tends to run in families and is often inherited from one or both parents.
- Are there any medical conditions that can cause female pattern baldness?
Yes, certain medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can contribute to female pattern baldness.
- Can lifestyle factors contribute to female pattern baldness?
Yes, factors such as stress, poor nutrition, and certain hairstyles (such as tight braids or ponytails) can contribute to hair loss in women.
- What are female pattern baldness treatment options?
There are several treatments available for female pattern baldness, including medications such as minoxidil and finasteride, low-level laser therapy, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, and hair transplant surgery.
- How effective are these treatments?
The effectiveness of these treatments can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the hair loss. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine which treatment option is best for you.
