Chronic skin conditions affect millions of individuals worldwide, causing discomfort, insecurity, and sometimes even severe health complications. These conditions can be persistent, requiring long-term management and care. In this comprehensive exploration of chronic skin conditions, we will delve into some of the most prevalent ones, including Rosacea, Acne, Eczema, Psoriasis, Vitiligo, Hair loss, and Melasma. We will also address the common question: Is eczema a chronic skin condition?
Understanding Chronic Skin Conditions
Chronic skin conditions are characterized by their persistent nature, often lasting for years or even a lifetime. These conditions may involve the skin’s immune system, genetics, and external triggers. They can affect people of all ages and backgrounds, significantly impacting their quality of life.
Rosacea: The Blushing Enigma
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and small, red, pus-filled bumps on occasion. It usually starts with flushing and progresses to persistent redness. While the exact cause of Rosacea is unknown, certain factors such as genetics, environment, and certain triggers such as spicy foods and alcohol can aggravate symptoms. Rosacea management entails lifestyle changes, topical medications, and, in some cases, oral antibiotics.

Acne: More Than Just a Teenage Problem
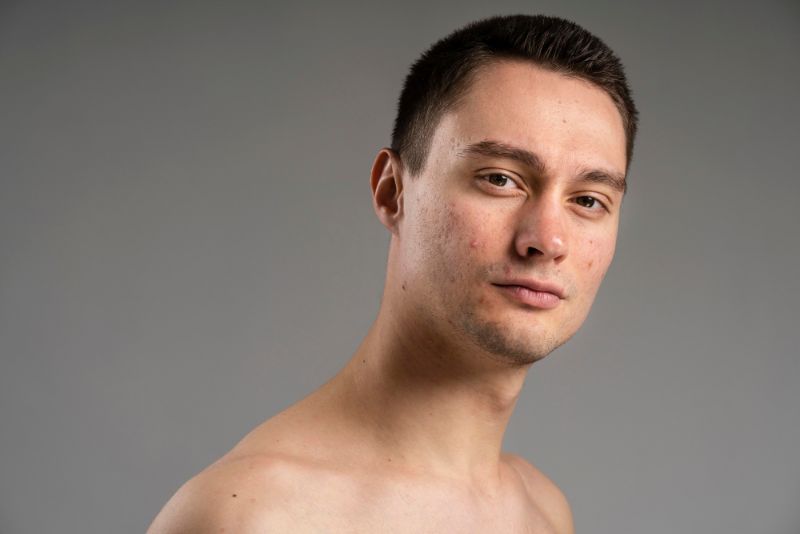
Acne is perhaps one of the most common chronic skin conditions, affecting people of all ages. It is distinguished by the presence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and, on rare occasions, cysts or nodules. While often associated with adolescence, acne can persist into adulthood. Hormonal imbalances, genetics, and improper skin care can contribute to its development. Treatment options range from topical creams to oral medications and lifestyle adjustments.

Eczema: Is It a Chronic Skin Condition?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that causes itchy, inflamed skin. It is often associated with a disrupted skin barrier and immune system dysfunction. Eczema can affect people of all ages, including infants. While eczema is indeed a chronic condition, symptoms can vary in severity and may even improve with age. Management involves moisturization, topical corticosteroids, and identifying and avoiding triggers.
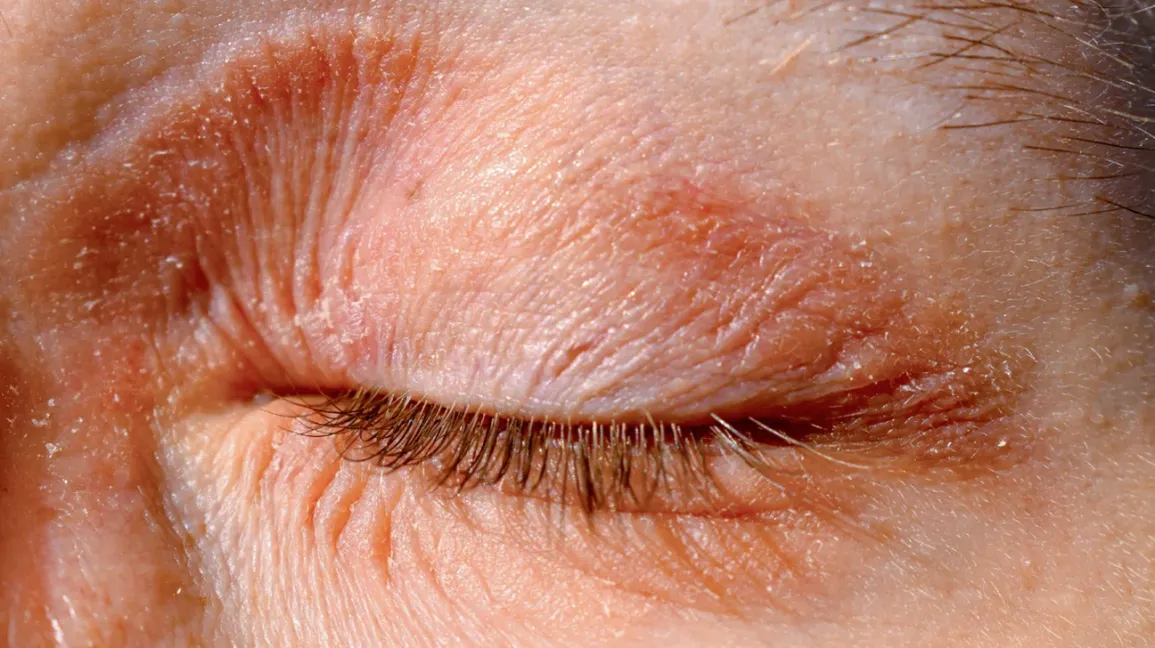
Psoriasis: The Scalp to Toe Challenge
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches to appear on the skin’s surface. It can affect any part of the body, including the scalp and nails. Psoriasis is linked to an overactive immune system, which triggers rapid skin cell turnover. While there is no cure, various treatments, including topical creams, phototherapy, and systemic medications, can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
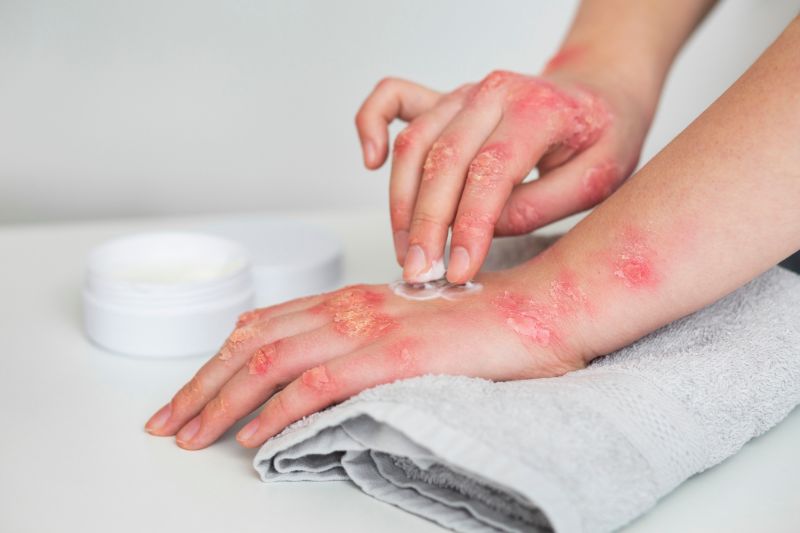
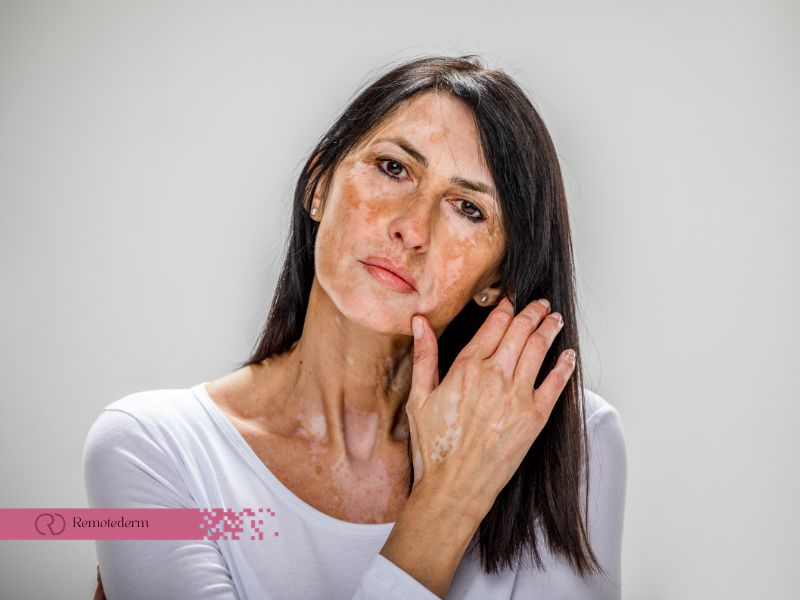
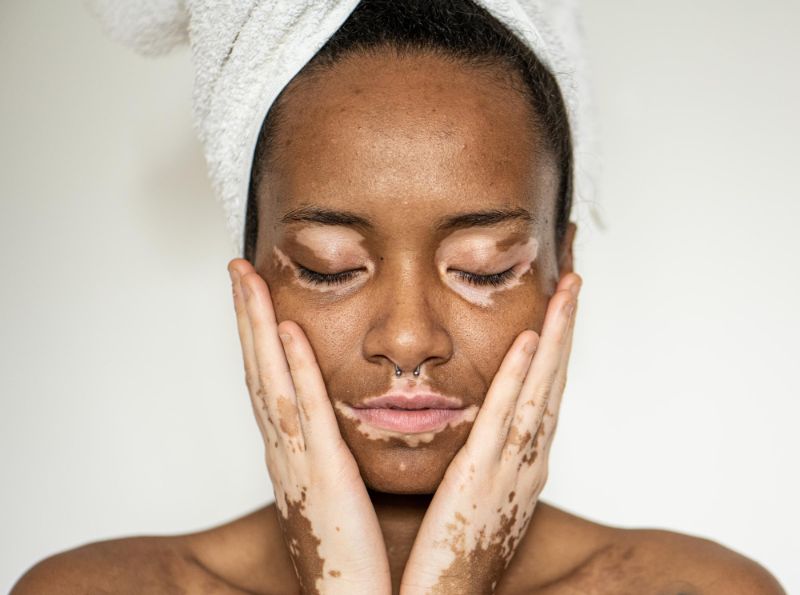
Vitiligo: The Puzzle of Pigment Loss
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition in which the skin loses pigment, resulting in white patches. The exact cause of vitiligo remains unclear, but it is believed to involve an autoimmune response against melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin colour. Treatment options vary and may include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, or skin grafting.

Hair Loss: When Skin Meets Scalp
Hair loss, although not always considered a chronic skin condition, often has a direct connection to the health of the scalp. Conditions like alopecia areata and androgenetic alopecia can lead to hair loss and can have a profound impact on self-esteem. Treatment options may include medications, topical solutions, and hair transplant surgery.
Melasma: The Mask of Pregnancy
Melasma is a chronic skin condition characterized by brown or greyish patches on the face, often triggered by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or birth control. While melasma is not a serious health concern, it can be emotionally distressing. Sun protection and topical treatments are commonly used to manage melasma.
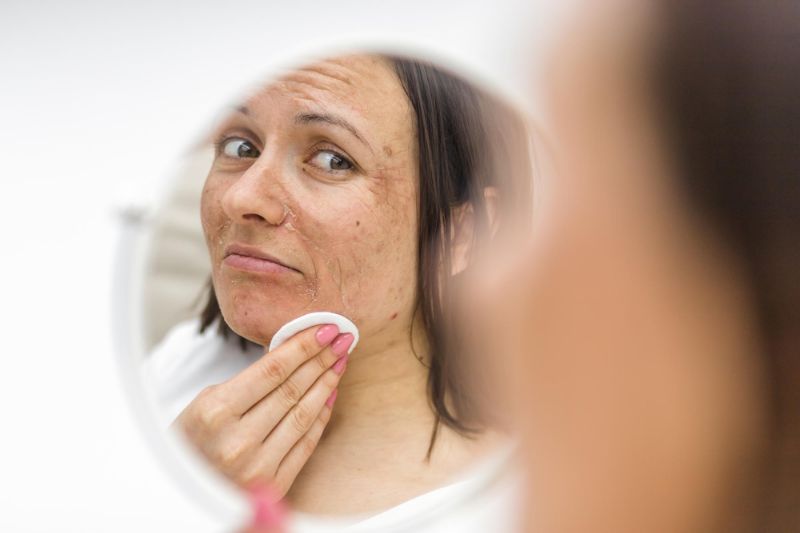

Chronic Skin Conditions Diagnosis
Diagnosing chronic skin conditions is a complex and nuanced process that requires the expertise of dermatologists and healthcare professionals. These conditions, which can range from psoriasis and eczema to vitiligo and chronic acne, often present with a wide spectrum of symptoms and manifestations. To effectively diagnose and manage chronic skin conditions, healthcare providers employ a combination of clinical assessment, medical history evaluation, and, in some cases, specialized tests and procedures.
- Clinical Assessment: A thorough clinical assessment is the cornerstone of diagnosing chronic skin conditions. Dermatologists rely on their expertise to visually inspect the affected skin, looking for distinctive characteristics such as rash patterns, color changes, and lesion types. The appearance, location, and distribution of skin abnormalities are crucial clues in pinpointing the specific condition.
- Medical History Evaluation: Gathering a detailed medical history is equally vital. Dermatologists inquire about factors like the onset and duration of symptoms, any potential triggers or aggravating factors, and the patient’s personal and family medical history. Information about previous skin conditions, allergies, and lifestyle habits can all provide valuable insights into the diagnosis.
- Biopsy and Laboratory Tests: In some cases, dermatologists may recommend biopsies or laboratory tests to confirm or refine the diagnosis. A skin biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the affected area, which is then examined under a microscope. This can help differentiate between conditions that share similar visual characteristics. Laboratory tests, such as blood tests or skin cultures, may also be conducted to detect underlying infections or autoimmune factors contributing to the skin condition.
- Advanced Imaging: In rare instances, advanced imaging techniques like dermatoscopy or confocal microscopy may be employed to gain deeper insights into the skin’s structure and potential abnormalities beneath the surface. These non-invasive methods aid in assessing the extent and depth of skin lesions.
- Allergy Testing: For individuals with suspected allergic skin conditions, allergy testing, such as patch testing or blood tests for specific allergens, can help identify triggers and allergens that may be exacerbating the skin condition.
Accurate diagnosis is fundamental to tailoring effective treatment plans and improving the quality of life for individuals living with chronic skin conditions.
Managing Chronic Skin Conditions
Managing chronic skin conditions is a comprehensive endeavour that requires a multifaceted approach aimed at not only alleviating symptoms but also enhancing overall skin health. The following strategies and treatments are integral components of this holistic management process:
- Skincare Routine: Establishing a gentle and consistent skincare regimen forms the foundation for managing chronic skin conditions. The meticulous selection of skincare products becomes pivotal, including the use of hypoallergenic moisturizers to maintain skin hydration. Additionally, steering clear of harsh soaps and opting for cleansers designed for sensitive skin can prevent further irritation. Sunscreen application is indispensable as it shields the skin from harmful UV rays that can exacerbate certain skin conditions.
- Topical Treatments: Many chronic skin conditions benefit from topical treatments, which are applied directly to the affected areas. These may include a variety of solutions, such as corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation in conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. Topical antibiotics can effectively combat bacterial overgrowth in skin conditions like acne.

- Oral Medications: In some instances, oral medications become imperative to control symptoms and manage chronic skin conditions. Dermatologists may prescribe antibiotics to combat infections associated with skin conditions or antihistamines to alleviate itching and discomfort. Immunosuppressants might be necessary for autoimmune skin disorders to modulate the immune response.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Beyond topical and oral interventions, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in maintaining skin health. Identifying and avoiding triggers that exacerbate skin conditions, such as allergens or stressors, becomes paramount. Furthermore, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients can bolster the skin’s ability to heal and regenerate, thereby contributing to long-term management.
- Laser and Light Therapies: In cases of stubborn skin conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo, healthcare professionals may recommend laser and light therapies. These innovative treatments target affected areas with precision, helping to mitigate symptoms and promote the rejuvenation of skin. Laser and light therapies are often employed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan to complement other modalities.
Managing chronic skin conditions requires a comprehensive approach. By integrating these strategies into a well-structured management plan, individuals can alleviate symptoms and foster healthier and more resilient skin in the face of chronic skin conditions.
Natural Remedies for Chronic Skin Conditions
Natural remedies for chronic skin conditions have gained popularity as people seek alternative approaches to complement conventional treatments. While these remedies may not replace medical interventions, they can often provide relief and support for managing chronic skin conditions. Here are some natural remedies to think about:
- Aloe Vera: The soothing and anti-inflammatory qualities of aloe vera plant gel are well known. In skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne, it can be applied topically to relieve itching and lessen redness.
- Coconut Oil: Fatty acid-rich coconut oil is a natural moisturizer. It can help reduce the symptoms of conditions like xerosis or dermatitis when applied to dry, flaky skin.
- Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal baths can help soothe itchy, irritated skin. They form a protective barrier on the skin’s surface and are useful for conditions such as eczema and contact dermatitis.
- Tea Tree Oil: Because tea tree oil has antibacterial and antifungal properties, it can be used to treat conditions such as acne and fungal infections. To avoid skin irritation, use it sparingly and diluted.
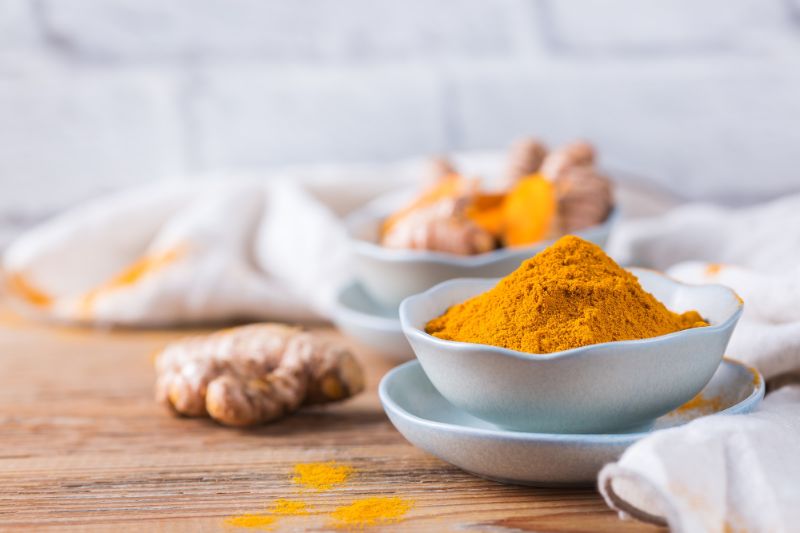
- Turmeric: Curcumin, found in turmeric, is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric and water paste can be applied to areas of inflammation in conditions such as psoriasis.

- Honey: Raw honey has natural antibacterial properties and can be applied topically to wounds or areas of infection to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Consuming omega-3 fatty acid-rich foods, such as fatty fish or flaxseeds, may help reduce inflammation associated with skin conditions such as eczema.
It’s essential to exercise caution and consult with a healthcare provider or dermatologist before attempting natural remedies, especially if you have severe or extensively spread chronic skin conditions. Some remedies may work better for specific conditions or individuals, and it’s crucial to monitor for any adverse reactions.
Final Thoughts,
In summary, chronic skin conditions can significantly impact individuals’ lives, causing discomfort and insecurity. This overview covered various conditions, including Rosacea, Psoriasis, Vitiligo, Hair Loss, and Melasma, while addressing the question of eczema’s chronic nature. Effective management starts with accurate diagnosis through clinical assessments, medical history evaluations, and specialized tests conducted by dermatologists and healthcare professionals.
Managing these conditions requires a multifaceted approach, including skincare routines, topical and oral treatments, lifestyle modifications, and, at times, advanced therapies. Natural remedies can provide relief but should be used cautiously. Ultimately, managing chronic skin conditions is a journey that demands persistence and a focus on improving quality of life. Consulting healthcare professionals is crucial for safe and effective management.
FAQs
- Can chronic skin conditions affect children?
Yes, chronic skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis can affect children, and early intervention is crucial.
- Can children outgrow chronic skin conditions like eczema?
Some children may outgrow eczema as they get older, but it varies from person to person, and it can persist into adulthood.
- Can chronic skin conditions be prevented?
While prevention may not always be possible, certain lifestyle choices and skincare practices can help reduce the risk and severity of chronic skin conditions.
- Can chronic skin conditions affect the nails and hair?
Yes, chronic skin conditions like psoriasis can affect the nails and scalp, leading to symptoms such as nail pitting and scalp scaling.
