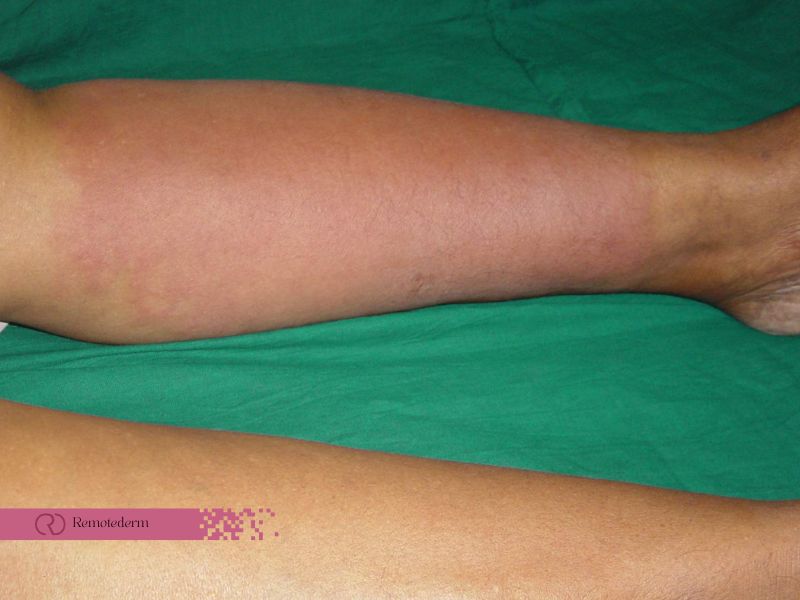
Cellulitis is a common and potentially serious bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues. It can occur anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on the legs, arms, and face. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cellulitis is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. In this article, we will explore what cellulitis is, its symptoms, when to worry, treatment options, and how to live with cellulitis.
What is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues. It is typically caused by bacteria entering the skin through cuts, cracks, or breaks. The bacteria streptococcus and staphylococcus are the most frequently found ones that cause cellulitis. This infection can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most commonly found on the legs, arms, and face.
Cellulitis is distinguished by the presence of localized redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. In more severe cases, it may be accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever and chills. Prompt medical attention is essential to prevent the infection from spreading or causing complications.
While cellulitis can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk, including a weakened immune system, chronic conditions like diabetes, obesity, and lymphedema, as well as recent surgery or injury.
Discover the underlying causes of eczema and gain insights into effective management strategies. Click to explore our informative article on eczema and its triggers.
Recognizing Cellulitis Symptoms
- Skin Redness and Swelling: Cellulitis typically presents as a localized area of redness, warmth, and swelling on the affected skin. The affected area may also feel tender or painful to touch.
- Spreading Rash: The redness and swelling of cellulitis may gradually spread over time. The rash may expand beyond the initial site of infection, and the edges of the affected area may appear raised and distinct.
- Skin Tightness: As cellulitis progresses, the skin in the affected area may become tight and shiny due to inflammation and swelling.
- Warmth and Increased Temperature: The skin over the infected area may feel warm to the touch and have an elevated temperature compared to the surrounding skin.
- Fever and Chills: In more severe cases, cellulitis may be accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, chills, fatigue, and malaise.
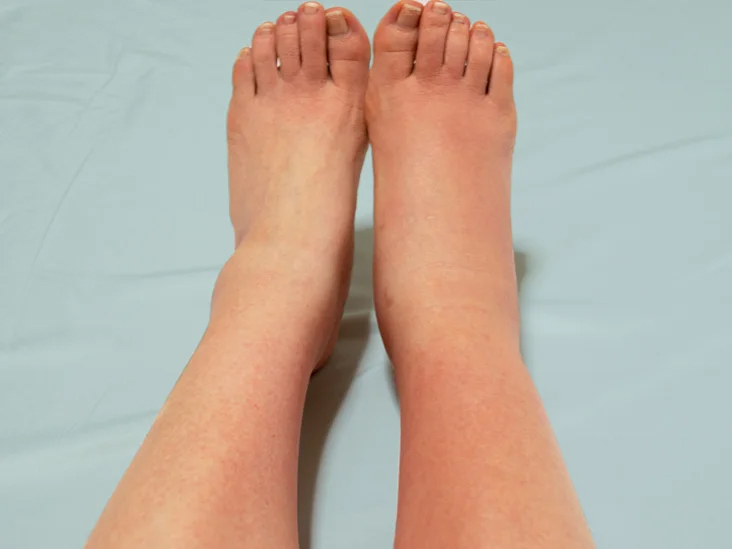
When to Worry?
While cellulitis is generally treatable, there are certain signs that should prompt immediate medical attention:
- Rapidly Spreading Rash: If the redness and swelling of cellulitis spread rapidly, especially within a few hours, it may indicate a severe infection requiring urgent medical care.
- Increasing Pain: If the pain in the affected area intensifies or becomes unbearable, it could be a sign of a deeper infection or abscess.
- Systemic Symptoms: If you develop a high fever, chills, or experience confusion, it is important to seek medical attention as these symptoms may indicate a severe infection or bloodstream involvement.
- Worsening Symptoms: If your symptoms do not improve or worsen despite treatment, it is important to consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Treatment Options for Cellulitis
Cellulitis treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics and self-care measures. The specific antibiotic prescribed will depend on the severity of the infection and the suspected bacteria causing it. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include penicillin, cephalosporins, or clindamycin. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your skin dermatologist to ensure the complete eradication of the infection.
In addition to antibiotics, the following self-care measures can help manage cellulitis symptoms and promote healing:
- Elevate the Affected Limb: If cellulitis affects the arms or legs, elevating the limb above the heart level can help reduce swelling and improve blood circulation.
- Apply Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. However, avoid using hot compresses, as they can worsen the infection.
- Take Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce fever associated with cellulitis.
- Keep the Area Clean and Moisturized: Gently cleanse the affected area with mild soap and water, then apply a moisturizing cream or ointment to prevent excessive dryness and cracking of the skin.
Living with Cellulitis
For individuals who have experienced cellulitis, taking steps to prevent future infections is crucial. Here are some tips for living with cellulitis:
- Practice Good Skin Care: Keep your skin clean and dry, paying extra attention to areas prone to moisture accumulation, such as skin folds or areas under compression garments.
- Moisturize Regularly: Applying a moisturizer regularly can help keep your skin healthy and less prone to cracking, reducing the risk of bacterial entry.
- Protect Your Skin: Use protective clothing, gloves, or footwear when engaging in activities that may increase the risk of skin injuries, such as gardening or working with sharp objects.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have any chronic conditions like diabetes or lymphedema, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively and reduce the risk of cellulitis.
- Stay Vigilant: If you notice any signs or symptoms of cellulitis, seek medical attention promptly to prevent the infection from worsening.

Conclusion
In conclusion, cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues. It is commonly caused by bacteria entering the skin through cuts, cracks, or breaks. Cellulitis typically presents with localized redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading or causing complications.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cellulitis is essential for early detection and timely treatment. If you notice any rapidly spreading rash, increasing pain, systemic symptoms like fever and chills, or worsening symptoms despite treatment, it is important to seek immediate medical care.
Treatment for cellulitis usually involves antibiotics and self-care measures. Completing the full course of antibiotics prescribed by your healthcare provider is crucial to ensure complete eradication of the infection. Self-care measures such as elevating the affected limb, applying warm compresses, taking pain relievers, and keeping the area clean and moisturized can help manage symptoms and promote healing.
For individuals living with cellulitis, practicing good hygiene, moisturizing regularly, protecting the skin, managing underlying conditions, and staying vigilant for any signs of infection is important for preventing future episodes.
FAQs
- Can cellulitis be prevented?
While it cannot be completely prevented, practicing good hygiene, protecting the skin, and managing underlying conditions can reduce the risk of developing cellulitis.
- What is the recovery time after cellulitis?
Cellulitis healing time varies according to the severity of the infection and individual circumstances. It usually takes a few days to weeks to recover with appropriate treatment.
- Can cellulitis come back after treatment?
Yes, cellulitis can recur, especially if risk factors like chronic conditions or skin injuries persist. Taking preventive measures is crucial to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Should I see a doctor if I suspect cellulitis?
Yes, it is important to see a healthcare provider if you suspect cellulitis or notice any concerning symptoms for proper diagnosis and treatment.