Eczema, which is also called atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that is chronic in nature, which means that it can last a long time. The statistics show that eczema has become one of the most common skin disorders in Canada and its prevalence is growing around the world. If you or someone you know has eczema, you may wonder, does eczema spread? This guide will talk about whether or not eczema is contagious, what the causes of it are, and how to treat it.
What Is Eczema?
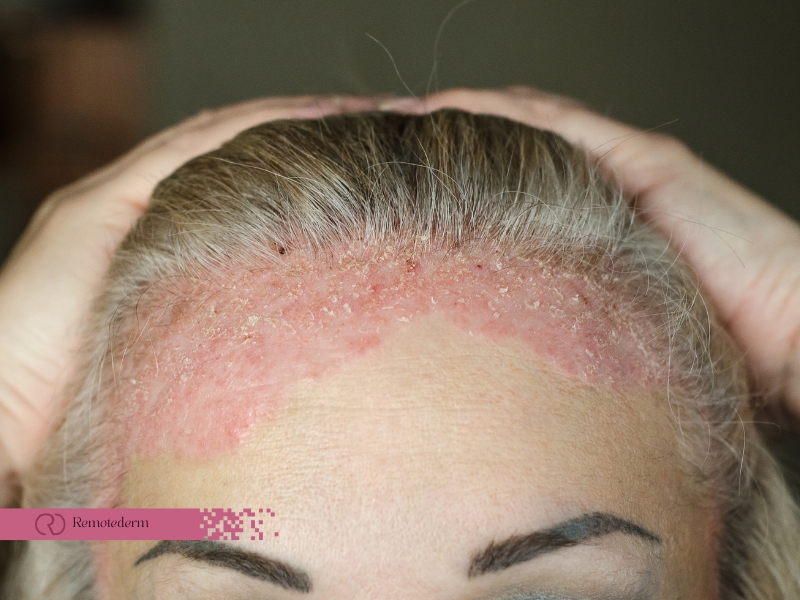
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that refers to an inflammation of the skin and it is characterized by dry, itchy, and swollen skin patches. It is most probably found in children to start with but can affect any person at any age if the conditions are met. The exact cause is not clear, but the genes and the environment are important factors.
Common Symptoms of Eczema:
Eczema symptoms can demonstrate in different degrees of severity and can look differently, but the most common ones are inflammation and irritation of the skin. These initial symptoms can be the basis of better management of the condition:
- Dry, scaly skin
- Red patches, often on hands, feet, and joints
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Thickened or cracked skin
- Raised bumps that may ooze when scratched
Does Eczema Spread?
Eczema is not contagious, so it doesn’t spread from person to person. However, it can appear to spread on your body.
How Eczema Appears to Spread?
Although eczema itself is not contagious, it can sometimes seem like it spreads across the skin or to new areas of the body. This is mainly due to certain behaviors or triggers that aggravate the condition, thereby making it appear as though it is spreading:
- Irritants: Strong soaps, allergens, and even weather changes can bring up new patches.
- Scratching: Scratching can make the already existing flares become new ones.
- Stress: Stress can be a significant factor for the worsening of eczema and thus cause it to appear in some new parts of the body.
Can Eczema Spread from Person to Person?
As mentioned, eczema is not something that can be transmitted from one individual to another. It is related to your immune system and heredity, which are not influenced by external factors such as infections.
Misconceptions About Eczema
People have some common misperceptions about eczema that create the necessity for a dermatologist to be consulted. They stem from the way eczema appears, which could be the case for any family.
- Appearance: Eczema may be confused with some other similar skin diseases that are, however, not contagious.
- Family History: Eczema is a clear hereditary trait, which may cause the belief that it is contagious in families.
How to Manage and Prevent Eczema Flare-Ups
Skincare, lifestyle improvements, and sometimes medications are involved in eczema management. Here’s a quick list of approaches to keeping your control:
1. Moisturize Regularly
An essential step for skin hydration and eczema control is to moisturize using potent creams or ointments, preferably after bathing. Such products should never be scented and you should use only ones made for sensitive skin.
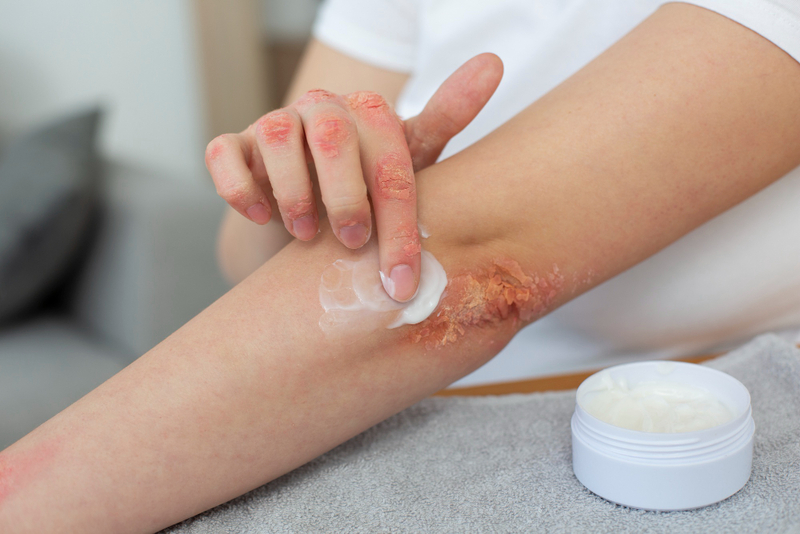
2. Identify and Avoid Triggers
If you can identify and stay away from common triggers such as soaps, wool, pollen, and certain foods then you can limit eczema flare-ups. Consider consulting an eczema dermatologist for patch testing to identify specific triggers.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Eating omega-3 rich foods such as fish and flax seeds can possibly lower the inflammatory process associated with eczema. Furthermore, stress-relief techniques like yoga or meditation can also help alleviate this condition.
4. Use Medications When Necessary
Topical corticosteroid creams are the most frequent medications used to deal with inflammation. In more serious situations, oral medication such as antihistamine or immunosuppressants may be used.
5. Protect Your Skin
To shield your skin and lessen the itching, choose soft, breathable fabrics such as cotton that are easy to wash. Besides, you should not take hot showers as hot water can dry your skin and worsen eczema symptoms.
Eczema in Canada
Eczema is prevalent in Canada where the cold and dry winters increase symptoms. Canadians should concentrate on regular moisturizing and also keeping their skin safe from extreme weather conditions. The management of this disease is assisted through the provision of healthcare services, including online eczema dermatologist services.
Final Thoughts
Eczema is a condition that is treated by the right care. When you get it, it does not spread from one person to another. However, the situation can worsen and new areas can be affected if the treatment is not done properly. Regularly applying skin care products, staying away from triggers, and consulting a dermatologist can help you keep eczema under control.
FAQs
1. Can eczema turn into infections?
Indeed, some skin infections may result from scratching the skin. It is most important not to scratch your nails too much during this period.
2. Is there a link between eczema and asthma?
Eczema is known as a chronic skin condition that often affects people with asthma or hay fever.
3. Can food cause eczema?
Yes. Foods like dairy, nuts, and gluten are the most common ones. They can be identified via an elimination diet conducted by a healthcare professional.
4. How do Canada’s climate conditions affect eczema?
The cold winters in Canada may cause skin to dry out and aggravate eczema as a result, thus frequent moisturizing will be required.