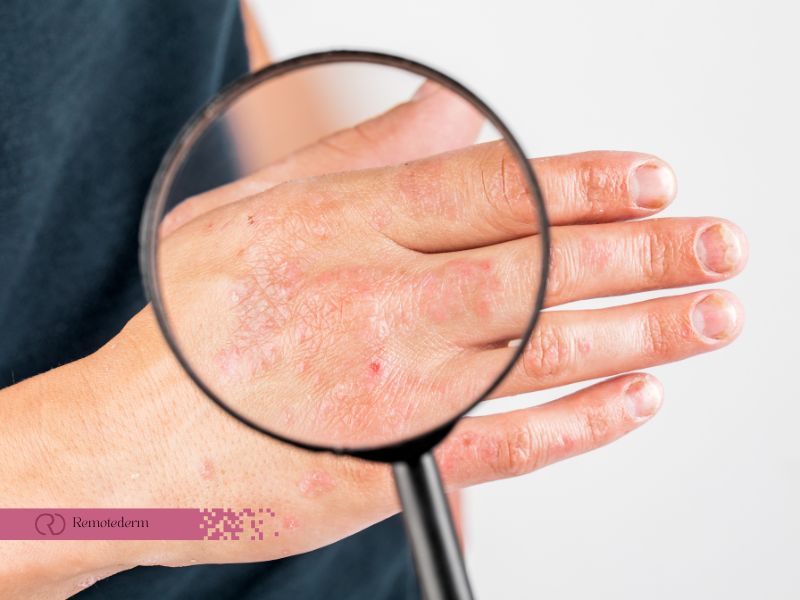
When it comes to skin conditions, dermatitis herpetiformis vs eczema are two commonly discussed skin conditions. Although they share some similarities, they are distinct conditions with different symptoms and triggers. Understanding the differences between eczema vs dermatitis herpetiformis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, triggers, and management strategies for both dermatitis herpetiformis and eczema.
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a persistent autoimmune skin disorder that causes extreme itching and burning. It is closely associated with celiac disease, a condition in which the body cannot tolerate gluten. Dermatitis herpetiformis is considered the skin manifestation of celiac disease, and both conditions share a common genetic link.
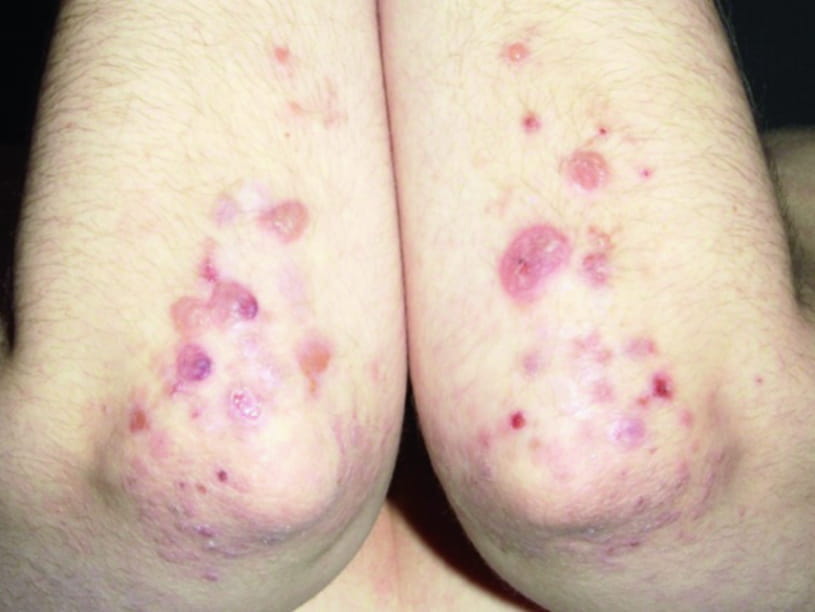
Symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
The primary symptom of dermatitis herpetiformis is the presence of clusters of small, red bumps and blisters on the skin. These blisters are typically extremely itchy and can be quite painful when scratched. The most commonly affected areas include the elbows, knees, buttocks, back, and scalp. Unlike eczema, which often presents as dry and scaly patches, dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by the presence of vesicles and papules.
Triggers of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
The exact cause of dermatitis herpetiformis is not yet fully understood, but it is known to be an autoimmune reaction triggered by gluten ingestion. When individuals with dermatitis herpetiformis consume gluten-containing foods, their immune system produces antibodies that mistakenly attack the skin, leading to the characteristic rash and blisters.
Eczema
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin illness that affects people of all ages. It is also known as atopic dermatitis. It is distinguished by dry, itchy, and irritated skin. Eczema is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and it often occurs in individuals with a family history of allergies or asthma.
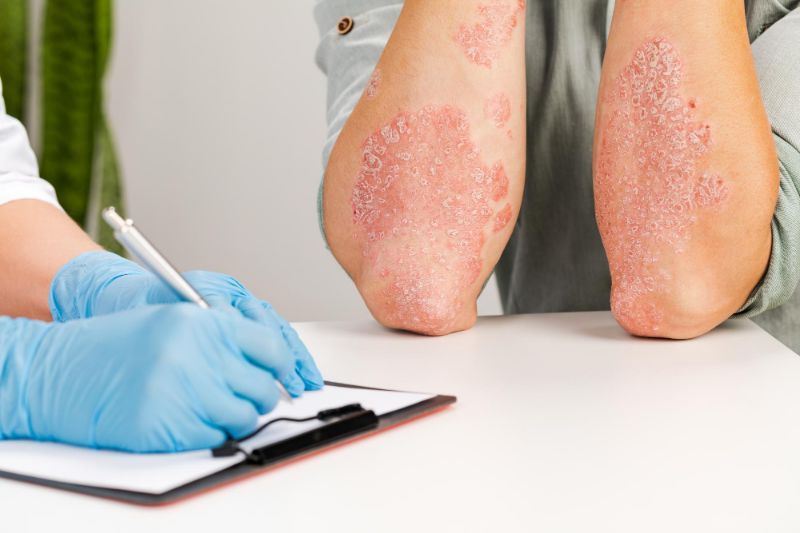
Symptoms of Eczema
The symptoms of eczema can vary from mild to severe, and they may include dryness and scaling of the skin, redness, itching, and the formation of small bumps or blisters. The affected areas can become swollen and develop crusts or oozing lesions due to scratching. Eczema commonly occurs on the face, hands, feet, and areas where the skin folds, such as the elbows and knees.
Triggers of Eczema
Eczema can be triggered by a range of factors, including allergens (such as pollen, pet dander, or certain foods), irritants (such as soaps, detergents, or harsh chemicals), temperature changes, stress, and hormonal fluctuations. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is essential in managing eczema and reducing flare-ups. Additionally, maintaining proper skin hydration through regular moisturization is important for individuals with eczema.
Dermatitis Herpetiformis vs Eczema
When it comes to skin conditions, dermatitis herpetiformis and eczema may share some similarities in terms of itchy skin and skin inflammation. However, several key differences can help distinguish between the two conditions, allowing for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Appearance
One of the primary differences lies in their appearance. Dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by clusters of small, red bumps and blisters on the skin. These clusters often cause intense itching and can be quite uncomfortable. On the other hand, eczema often presents as dry, scaly patches or raised, oozing lesions. The skin affected by eczema may have a rough texture and can become red and inflamed.
Affected Areas
Another distinguishing factor is the location of the affected areas. Dermatitis herpetiformis commonly affects areas such as the elbows, knees, buttocks, back, and scalp. These regions are prone to the appearance of characteristic clusters of bumps and blisters. In contrast, eczema can occur on various parts of the body but is frequently found on the face, hands, feet, and skin folds, such as the elbows and knees.
Triggers
The triggers for these conditions also differ. Dermatitis herpetiformis is triggered by the ingestion of gluten, which is found in wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten triggers antibodies that attack the skin, causing rash and blisters in dermatitis herpetiformis.
Eczema, on the other hand, can be triggered by a variety of factors. Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, certain foods, or even environmental irritants can provoke eczema symptoms. Additionally, temperature changes, stress, and hormonal factors can contribute to flare-ups in individuals with eczema.
It’s worth noting that dermatitis herpetiformis is closely associated with celiac disease, a condition in which the body cannot tolerate gluten. Both dermatitis herpetiformis and celiac disease share a common genetic link. In contrast, eczema often coexists with other allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever. The presence of these associated conditions can provide additional insights for healthcare professionals during diagnosis and treatment planning.
By understanding these differences between dermatitis herpetiformis and eczema, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention, follow the recommended treatment strategies, and effectively manage their symptoms. Accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are crucial, so it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and guidance.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for any specific concerns or questions related to your own condition. For individuals seeking prompt and convenient skin dermatologist consultation, RemoteDerm offers online services that eliminate the long waits associated with in-person visits to a dermatologist.
Treatment and Management
The treatment approaches for dermatitis herpetiformis and eczema differ due to their distinct underlying causes and triggers.
Dermatitis Herpetiformis Treatment
A strict gluten-free diet is the primary treatment for dermatitis herpetiformis. By eliminating gluten from the diet, individuals can prevent the autoimmune reaction that leads to skin symptoms. In addition to dietary changes, dermatologists may prescribe medications such as dapsone or sulfapyridine to manage the skin rash and alleviate itching. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional are essential to monitor the condition and ensure optimal management.

Eczema Treatment
The treatment of eczema aims to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and restore the skin’s barrier function. It typically involves a combination of measures, including skin care (the use of moisturizers to hydrate the skin), topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators to reduce inflammation, and antihistamines to alleviate itching. Systemic medicines or phototherapy may be recommended in extreme situations. Working together with an eczema dermatologist or healthcare professional to build a specific treatment strategy for eczema control is critical.
Conclusion
Dermatitis herpetiformis and eczema are distinct skin conditions with different symptoms, triggers, and treatment approaches. While dermatitis herpetiformis is closely associated with celiac disease and triggered by gluten ingestion, eczema is a chronic inflammatory condition influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
By understanding the characteristics of each condition, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention, follow the recommended treatment strategies, and effectively manage their symptoms. If you suspect you have either dermatitis herpetiformis or eczema, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
FAQs
- Can eczema and dermatitis herpetiformis coexist?
It is possible, as individuals with eczema may also have other allergic conditions, but a proper diagnosis is important to differentiate between the two.
- Can dermatitis herpetiformis be managed without a gluten-free diet?
No, a strict gluten-free diet is the cornerstone of managing dermatitis herpetiformis.
- Is dermatitis herpetiformis a common condition?
Dermatitis herpetiformis is considered rare, affecting a smaller percentage of the population compared to eczema.
- Are there any complications associated with dermatitis herpetiformis?
If left untreated or poorly managed, dermatitis herpetiformis can lead to long-term complications, such as scarring and skin discolouration.