Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts on the skin. They can appear suddenly and can be caused by a variety of factors. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hives.
Hives are a skin condition that results in red, itchy welts on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body and can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Hives can last for a few minutes to several days, and in some cases, they can recur for weeks or even months.
What is Hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts on the skin. These welts can appear anywhere on the body and can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. They can appear suddenly and can be caused by a variety of factors such as allergens, viral infections, stress, and certain medical conditions. Hives can be classified into two types: acute and chronic. Acute hives last for less than six weeks, while chronic hives last for more than six weeks.
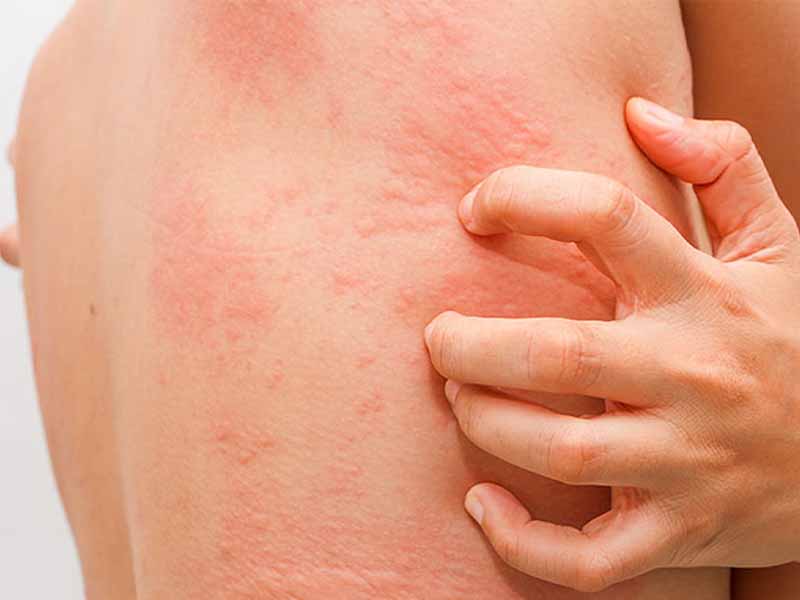
Symptoms of Hives
The most common symptoms of hives include red, itchy welts on the skin. These welts can appear suddenly and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, as well as difficulty breathing. In some cases, hives can also cause a burning or stinging sensation on the skin.
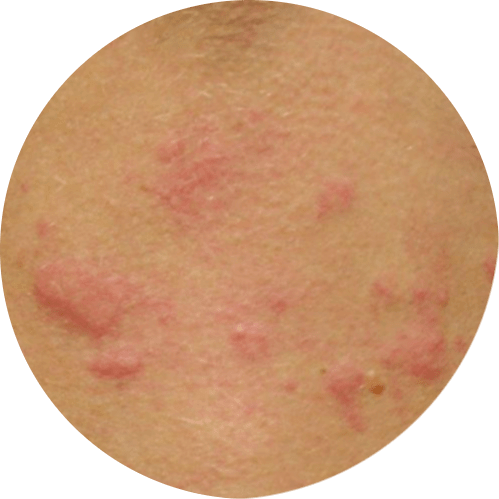
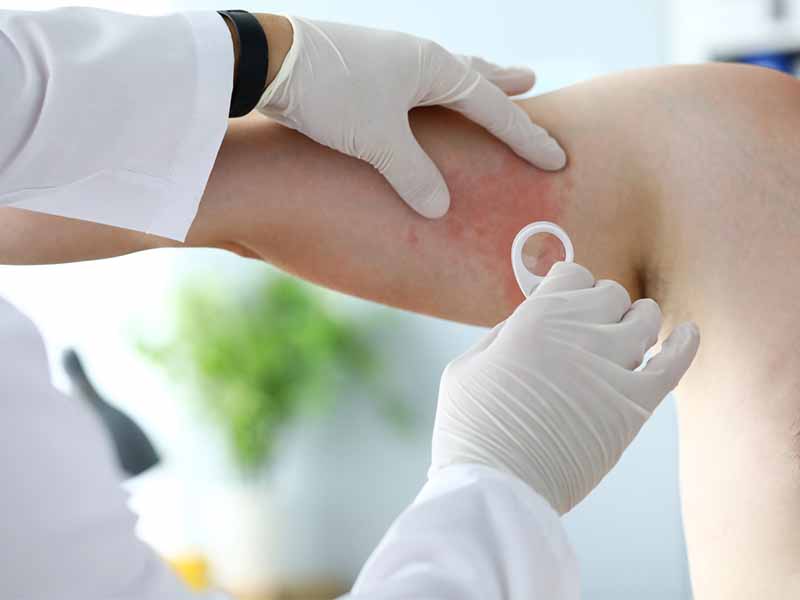
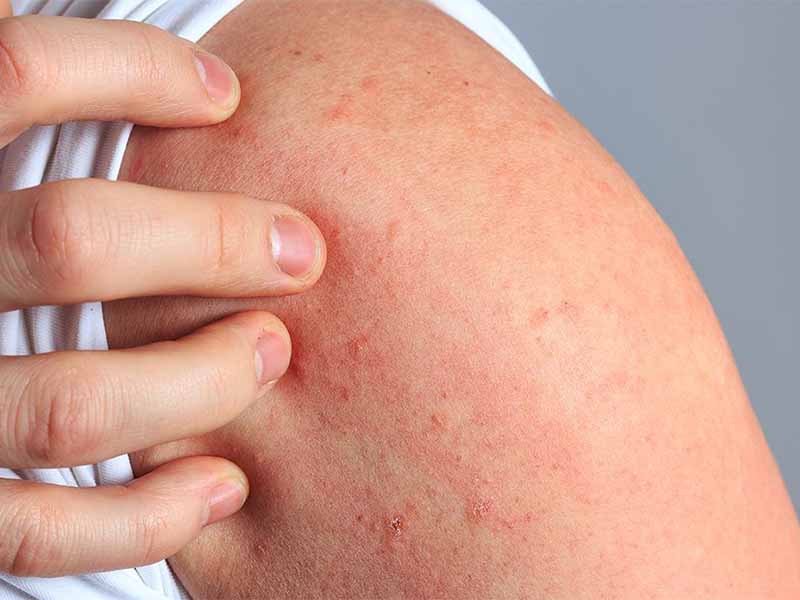
One of the main symptoms of hives is the presence of raised, red welts on the skin, which can be itchy and uncomfortable. These welts can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, arms, legs, and torso. They can vary in size, shape, and color, and can appear alone or in groups. They can also change in shape and size over time, which can make it difficult to identify the underlying cause of the hives.
Another symptom of hives is swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, which can occur in some cases. This is known as angioedema, and it can make it difficult to breathe, which can be a medical emergency. This swelling can also occur in other parts of the body such as hands, feet, and genitals.
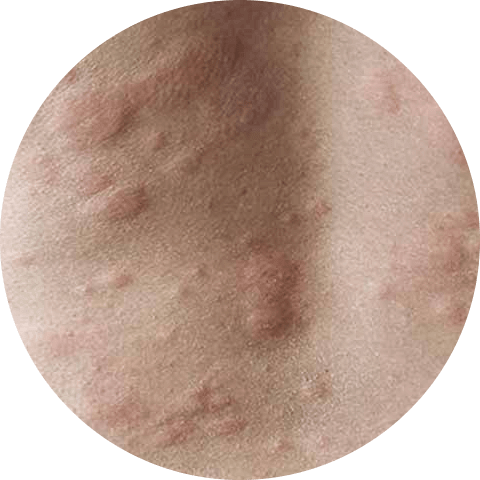
In addition to these symptoms, hives can also be accompanied by other symptoms such as a burning or stinging sensation on the skin, as well as a general feeling of discomfort and itchiness. These symptoms can be mild or severe, and can vary from person to person.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of Hives vary in severity it’s important to see a doctor if the hives are severe or if they are accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty breathing.
Causes of Hives
Hives can be caused by a variety of factors. The most common causes of hives include:
- Allergens, such as food, drugs, and insect stings. Allergic reactions can cause the release of histamine, which leads to the formation of hives on the skin.
- Food allergies are a common cause of hives, with common triggers including shellfish, nuts, eggs, and milk. Medications such as antibiotics, painkillers, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can also cause hives as an allergic reaction.
- Another cause of hives is viral infections such as the common cold, flu, and hepatitis. These infections can cause the release of histamine, leading to the formation of hives.
- Physical factors such as heat, cold, pressure, and sunlight can also cause hives. This is known as physical urticaria and can be caused by exposure to cold, heat, pressure, or sunlight.
- Stress can also be a cause of hives, as it can lead to the release of histamine in the body. Chronic stress can also make hives worse if they are already present.
- Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, can also be a cause of hives. These conditions can cause the immune system to attack the body’s own tissues, leading to the formation of hives.
- In some cases, the cause of hives is unknown. This is known as idiopathic urticaria and can be caused by a combination of factors.
Hives can have a variety of causes, and it can be challenging to identify just one of them. It’s crucial to see a dermatologist if you experience recurrent hives, so they can determine the root of the problem and provide the proper care.
You can get more information about online dermatology consultation by click on the link.
Hives Risk Factors
Hives can affect anyone, however, some people are at a higher risk of developing hives than others.
- One of the main risk factors for hives is a history of allergies. People who have a history of allergies, such as hay fever, asthma, or eczema, are more likely to develop hives.
- Another risk factor for hives is a family history of hives. If a family member has a history of hives, there is an increased chance of developing hives.
- Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing hives. Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of developing hives.
- Obesity is a risk factor for hives, as it can put extra pressure on the skin and increase the likelihood of developing hives.
- People who are exposed to certain environmental factors such as extreme temperature or humidity, or who work in certain jobs such as farming or construction, may be at a higher risk of developing hives.

Keep in mind that having one or more of these risk factors does not guarantee that a person will develop hives, but it increases the chances.
Treatment of Hives
Treatment for hives depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, hives will resolve on their own without treatment. However, if the hives are severe or if they are caused by an underlying medical condition, treatment may be necessary.

- Over-the-counter antihistamines can help to relieve the itching and redness associated with hives. These medications work by blocking the effects of histamine, which is a chemical that causes inflammation and itching. Some examples of over-the-counter antihistamines include diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and loratadine (Claritin).
- In more severe cases, prescription medications, such as corticosteroids, may be necessary. These medications can help to reduce inflammation and itching and are often used in cases where over-the-counter antihistamines are not effective.
- Immunomodulators such as omalizumab can be used in case of chronic spontaneous urticaria, that is not responsive to antihistamines.
- In cases where hives are caused by an underlying medical condition, treatment may focus on managing that condition. For example, if hives are caused by an autoimmune disorder, treatment may involve medications to suppress the immune system.
- In addition to medications, certain lifestyle changes can also help to alleviate the symptoms of hives. These include avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods, drugs, and insect stings, as well as practicing stress management techniques, such as yoga and meditation.
If your hives are severe or recurring, you should see a doctor because they could be a sign of an underlying medical condition that needs to be treated. The doctor can assist in determining the root cause of the hives and recommending appropriate treatment options.
Home Remedies for Hives
Home remedies can be an effective way to alleviate the symptoms of hives, also known as urticaria. Here are a few home remedies that may help to reduce the itching and inflammation associated with hives:
- Oatmeal Bath: Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to soothe itchy skin. Adding oatmeal to a warm bath can help to reduce the itching and redness associated with hives.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help to reduce the itching and inflammation associated with hives. Place a cold pack or a bag of frozen vegetables on the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Calamine lotion: Calamine lotion can be applied to the affected area to reduce itching and inflammation. This lotion can be found in any drugstore.
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce itching and inflammation associated with hives. Applying aloe vera gel to the affected area can provide relief from itching and redness.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding known triggers of hives such as certain foods, drugs, and insect stings can help to prevent hives from recurring.

These home remedies may provide temporary relief, and it’s important to consult with a doctor if the hives are severe or recurrent.
How to prevent Hives
As mentioned, Hives can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergic reactions, viral infections, and certain medications. To prevent hives, it is important to identify and avoid any triggers that may be causing them.
- One way to prevent hives is to avoid known allergens, such as certain foods, pollen, and pet dander. If you are unsure what is causing your hives, it may be helpful to keep a diary of your symptoms and what you were exposed to before the hives appeared. This can help you identify potential triggers and avoid them in the future.
- It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet and getting regular exercise. Stress can also be a trigger for hives, so it is important to find ways to manage stress, such as through yoga, meditation, or therapy.
- In addition, it is important to keep your skin moisturized and avoid hot baths or showers, as they can dry out your skin and make hives worse. If you have a more severe case of hives, your healthcare provider may recommend oral or topical corticosteroids to help reduce inflammation.

Finally, preventing hives can be done by identifying and avoiding triggers, taking antihistamines, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, keeping skin moisturized, and reducing stress. Also, if hives last more than six weeks, it is important to see a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.
Diagnosis of Hives
The diagnosis of hives typically begins with a physical examination and a detailed medical history. During the physical examination, a healthcare provider will examine the skin to look for raised, red, itchy welts. They may also ask about other symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, which can indicate a more severe allergic reaction.
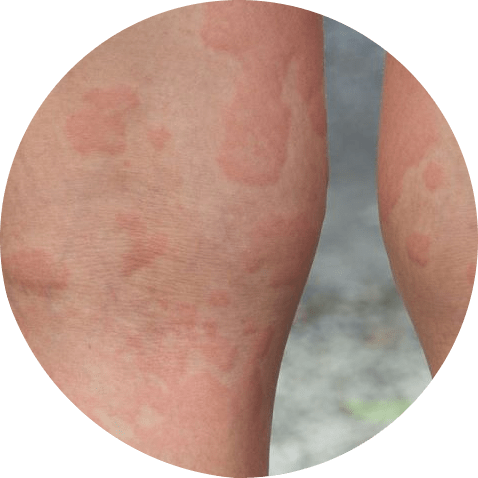
To determine the cause of hives, the healthcare provider may ask about any recent exposures to potential triggers, such as certain foods, medications, or environmental factors. They may also ask about any recent illnesses or infections, as viral infections can sometimes cause hives.
To further evaluate the cause of hives, the healthcare provider may order blood tests to check for allergic reactions, such as a total IgE level and specific IgE tests to detect allergies to specific substances. They may also order a skin prick test, in which a small amount of the suspected allergen is placed on the skin to see if it causes a reaction.
If the cause of hives is not clear, the healthcare provider may refer the patient to an allergist or immunologist for further evaluation. They may also order additional tests, such as a CT scan or an MRI, to rule out underlying medical conditions that may be causing hives.
In cases where the hives last more than six weeks, the healthcare provider may refer the patient to a rheumatologist or a dermatologist for further evaluation.
When to see a doctor?
As mentioned, you must see a healthcare provider if your hives last for more than six weeks, as this type of hives is called chronic urticaria, and requires further evaluation and treatment.
- Additionally, if you have hives that are accompanied by difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or a rapid heartbeat, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as these symptoms may indicate a more severe allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis.
- If your hives are causing severe itching or pain, it is also a good idea to see a healthcare provider, as they may be able to prescribe medication to help relieve these symptoms.
- If you have hives and a fever, this could be a sign of an underlying infection and it is important to see a healthcare provider.
- If you have hives and other symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, abdominal pain, or a rash, it may be helpful to see a healthcare provider, as these symptoms may indicate an underlying autoimmune disorder.
- If you are taking a medication and develop hives as a side effect, it is important to stop taking the medication and see a healthcare provider, as they may be able to prescribe an alternative medication.
Conclusion
Hives are a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts on the skin. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergens, viral infections, stress, and certain medical conditions. It’s important to see a doctor if the hives are severe or if they are accompanied by other symptoms such as difficulty breathing. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hives can help individuals manage this condition effectively. The most important thing is to identify the underlying cause of the hives, which can be done through a physical examination, medical history, and tests if necessary. With the right treatment, hives can be managed effectively, and individuals can enjoy a better quality of life.
Hives FAQs
1. Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious. Hives are a skin condition that results from an allergic reaction or other underlying medical condition. They are not caused by a contagious organism and cannot be spread from person to person through contact or other means.
2. Can hives be treated?
Yes, hives can be treated. The treatment for hives will depend on the underlying cause of the condition. Over-the-counter antihistamines can be used to reduce inflammation and itching associated with hives.
3. Do hives go away on their own?
Hives can go away on their own, but it depends on the underlying cause of the hives and the duration of the hives. Acute hives, which last less than 6 weeks, generally go away on their own.
4 comments
I get hives frequently, especially during allergy season. Is there a way to differentiate hives from other skin rashes?
Hives typically present as raised, itchy, and red bumps or welts on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body and may change in size and shape (check article’s images). They can also come and go quickly, and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as itching or burning.
I have heard that stress can cause hives. Can you provide more information on this connection?
Yes, stress can trigger hives in some people. When you experience stress, your body releases histamine, which can lead to hives. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises may help prevent stress-induced hives.