Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterised by the development of red, scaly patches on the skin. These patches can be itchy, painful, and unsightly, causing significant discomfort and embarrassment for those who suffer from them. Despite its prevalence, many people still have misconceptions about psoriasis and are not aware of the various treatments and management options that are available to them.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different symptoms, causes, types, and treatments for psoriasis, and provide you with practical tips and advice to help you live with this condition.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease characterised by red, raised, and scaly patches on the skin. Chronic plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis and is characterised by well-defined, erythematous (red) plaques with overlying, coarse scales. Other types of psoriasis include guttate, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Psoriasis is also associated with multiple comorbidities, including psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, diabetes, and atherosclerotic disease. It is important to screen for these comorbidities (having two or more diseases at the same time) in individuals with psoriasis.
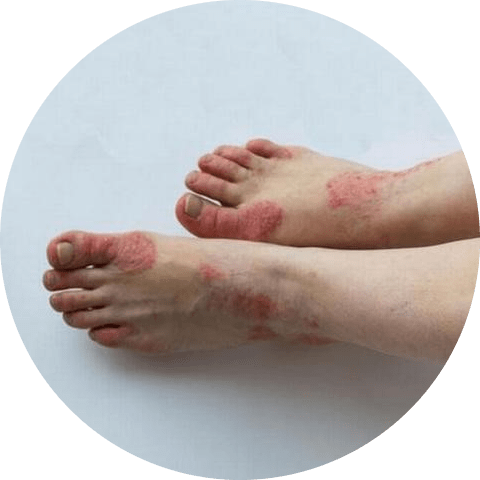
Understanding the Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis vary from person to person, but the most common signs include:
- Red, scaly patches on the skin called plaques
- Itching and burning sensation in the affected areas
- Thick, crusted sores that may bleed or become infected
- Joint pain and stiffness (in some cases)
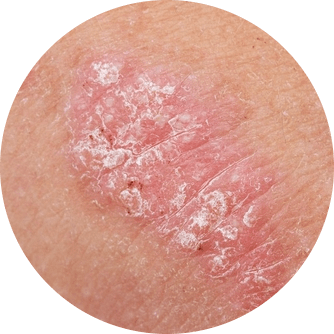
It is important to note that not all people with psoriasis will experience all of these symptoms. Additionally, the severity and frequency of symptoms can also vary, with some people experiencing occasional outbreaks and others suffering from persistent symptoms.
Discovering the Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the most common triggers for psoriasis outbreaks include:
- Injury to the skin
- Infections
- Weather changes
- Family history of psoriasis
- Weak immune system
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress
- Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarials
Psoriasis Risk Factors
There are several risk factors for psoriasis, including:
- Family history of psoriasis
- Age (psoriasis is most common in people between the ages of 15 and 35)
- Gender (men and women are equally affected by psoriasis)
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Stress
Identifying the Different Types of Psoriasis
There are several different types of psoriasis, each with its own unique set of symptoms and characteristics. Some of the most common types include:
- Plaque psoriasis
- Guttate psoriasis
- Inverse psoriasis
- Pustular psoriasis
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
There are various treatment options available for psoriasis, including both topical and systemic treatments. The most appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of the condition, the type of psoriasis, and the individual’s personal preferences.
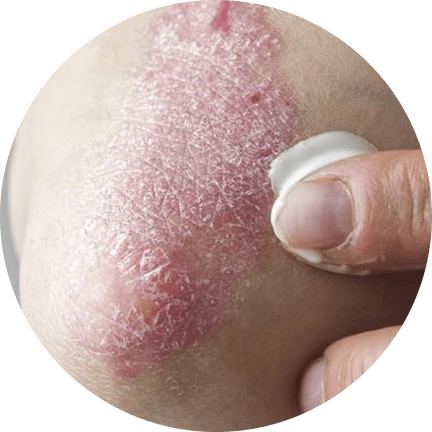
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments for psoriasis include creams, ointments, and gels that are applied directly to the skin. These treatments can help reduce inflammation, slow the production of skin cells, and relieve itching and pain. Some of the most commonly used topical treatments for psoriasis include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and calcineurin inhibitors.
Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments for psoriasis are medications that are taken orally or injected into the bloodstream. These treatments are used for moderate to severe cases of psoriasis and can help to reduce inflammation throughout the body. Some of the most commonly used systemic treatments for psoriasis include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biological drugs.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, is another treatment option for psoriasis. This involves exposing the affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light, which can help to reduce inflammation and slow the production of skin cells. Phototherapy is usually performed in a dermatologist’s office and can be done alone or in combination with topical or systemic treatments.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, there are also various lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis. These include maintaining a healthy diet, reducing stress, and avoiding triggers that can cause flare-ups. It is also important to keep the skin moisturised and protected from the sun, as UV light can worsen symptoms.
If you’re struggling to find effective relief from your psoriasis symptoms and home remedies aren’t providing the results you need, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist for psoriasis prescription and personalized guidance. At RemoteDerm, our specialized dermatologists are experienced in diagnosing and addressing the root causes of psoriasis. Take the first step towards managing your skin condition effectively by getting an online consultation with our dedicated specialists in Canada.
Home Remedies for Psoriasis
In addition to medical treatments, there are several home remedies that can help manage symptoms of psoriasis:
- Keep skin moisturised: Using a thick moisturiser can help soothe itchy skin and reduce the formation of plaques.
- Avoid triggers: Triggers such as stress, alcohol, and certain foods can worsen psoriasis symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms.
- Bath with colloidal oatmeal: Colloidal oatmeal can be added to bathwater to soothe itchy skin.
- Apply aloe vera: Aloe vera can be applied to affected areas to soothe skin and reduce inflammation.
- Use tea tree oil: Tea tree oil has antiseptic properties that can help reduce inflammation and soothe itchy skin.

How to Prevent Psoriasis
Preventing psoriasis can be challenging as the exact cause of the condition is not yet known. However, there are several lifestyle changes and strategies that you can implement to reduce your risk of developing psoriasis or to prevent the condition from becoming more severe.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help to improve your overall health and well-being and reduce your risk of developing psoriasis. Avoid processed foods and foods high in sugar, salt, and fat as these can worsen your symptoms.
- Manage stress: Stress can be a trigger for psoriasis and can worsen symptoms, so it is important to find ways to manage stress in your life. This may include practising relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, or finding healthy ways to cope with stress, such as exercise or talking to a friend.
- Avoid triggers: Certain triggers, such as alcohol, smoking, and certain medications, can worsen symptoms of psoriasis. It is important to identify your personal triggers and avoid them as much as possible.
- Keep your skin healthy: Maintaining healthy skin can help to prevent the development of psoriasis or to prevent the condition from becoming more severe. This may include using a gentle skin care routine, avoiding hot showers and baths, and using a humidifier to keep your skin hydrated.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help to improve your overall health and well-being and can also help to reduce stress and manage symptoms of psoriasis. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity each day, such as brisk walking, running, or cycling.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing psoriasis and can also worsen symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help to reduce your risk of developing psoriasis.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
A physical examination can be used to diagnose chronic plaque psoriasis in the vast majority of patients. A skin biopsy can be useful in difficult cases, but it is not always necessary. Other laboratory tests do not confirm the diagnosis. Genetic testing is not used to diagnose psoriasis.
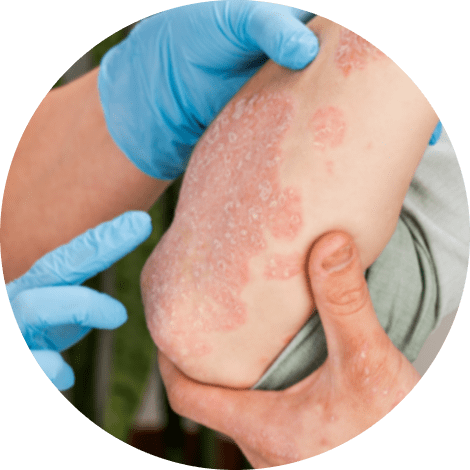
- History and physical examination: Patients with suspected chronic plaque psoriasis should receive a full skin examination that includes an examination of the scalp, nails, and anogenital skin. Chronic, well-demarcated, inflamed plaques with coarse scales are common on examination, especially when the scalp, ears, elbows, knees, and umbilicus are involved. In difficult cases, recognizing characteristic nail disease or inverse psoriasis in the intergluteal cleft or other sites can help support a psoriasis diagnosis.
Inquiries about a family history of psoriasis and exposure to medications that may induce or exacerbate psoriasis can be useful patient history questions.
- Skin biopsy: If the diagnosis is still uncertain after the history and physical examination, a skin biopsy may be performed. A 4 mm punch biopsy from the involved skin is typically performed, though a shave biopsy through the mid-dermis may also suffice. The specimen’s periodic acid-Schiff-diastase (PAS-D) stain may help distinguish psoriasis from a superficial fungal infection.
When to see a doctor?
If you are experiencing symptoms of psoriasis, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Early treatment can help to prevent the condition from becoming more severe and can also help you to manage your symptoms more effectively. In some cases, psoriasis may be mild and may not require medical treatment, but in other cases, it may be more severe and may require ongoing care and management.
If you are experiencing symptoms such as red, raised, and scaly patches on your skin, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Your doctor can examine your skin and make a diagnosis based on your symptoms and the appearance of your skin. They may also perform tests, such as a skin biopsy, to confirm the diagnosis.
In addition to seeking medical treatment for your psoriasis, there are also several lifestyle changes that you can make to help manage your symptoms. For example, maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding triggers that can worsen your symptoms, such as stress, alcohol, and smoking, can help to improve your overall health and well-being.
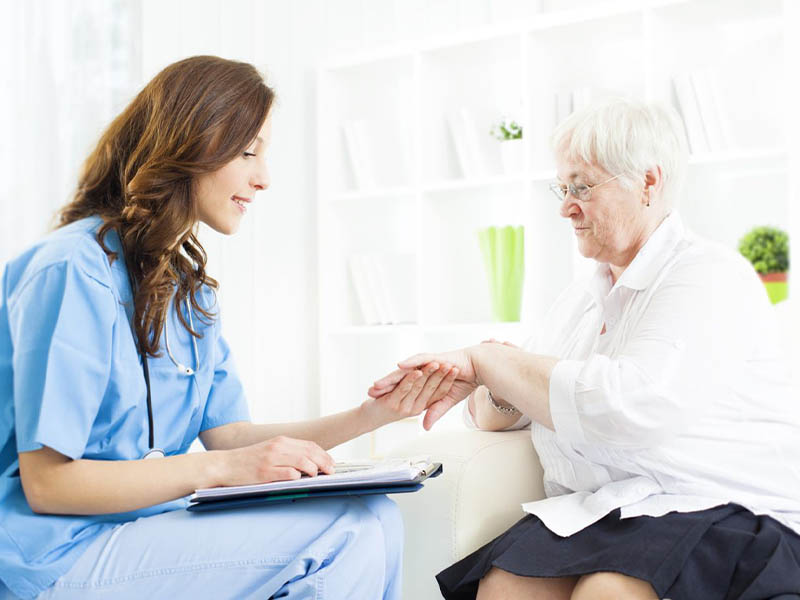

If you have psoriasis, it is also important to seek treatment for any related comorbidities, such as psoriatic arthritis or obesity, as these conditions can impact your overall health and quality of life. Your doctor can work with you to develop an individualised treatment plan that takes into account your specific needs and health status.
You can get information about online dermatology consultation by click on the link.
Conclusion
To summarise, psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can have a significant impact on those who suffer from it. Understanding the symptoms, causes, types, and treatments of psoriasis is critical for effective disease management. It is possible to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve the overall quality of life with the right treatment plan. It is critical to be proactive in determining what works best for you, whether through medical treatments, lifestyle changes, or home remedies. Living with psoriasis can be difficult, but with the right support and care, the condition can be managed and a fulfilling life can be lived.
Psoriasis FAQs
1. Is psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious. It is a chronic autoimmune condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
2. Can psoriasis go away on its own?
In some cases, psoriasis may go into remission without treatment. However, it is typically a chronic condition that requires ongoing treatment to manage symptoms.
3. What is the best treatment for psoriasis?
The best treatment for psoriasis will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual’s preferences and needs. Some of the most common treatments for psoriasis include topical creams and ointments, phototherapy, oral medications, and biological medications.
4. Can diet affect psoriasis?
While diet is not a direct cause of psoriasis, certain foods can trigger flare-ups in some people. It is important to work with a doctor or dietitian to determine if there are any specific foods that trigger your symptoms.
5. Is there a cure for psoriasis?
Currently, there is no cure for psoriasis. However, there are many treatments that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.

4 comments
I’ve heard that stress can trigger psoriasis symptoms. Are there any specific stress management techniques that you would recommend for people with psoriasis?
Yes, stress can be a trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. We recommend various stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to help manage stress levels and reduce the risk of triggering psoriasis symptoms.
Hi, is it possible to develop psoriasis later in life or is it only something that people are born with?
Hello Maria, Psoriasis can develop at any age, although it typically first appears between the ages of 15 and 35. It’s not something that people are born with, but rather something that develops due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.