Impetigo, a common bacterial skin infection, can be a pesky and contagious menace, particularly among young children in close-contact settings like schools and daycares. But fear not! In this in-depth guide, we’ll delve into the different types of impetigo, their telltale symptoms, and the most effective treatment methods.
Whether you’re a parent concerned about your child’s well-being or an adult looking to safeguard your skin health, this article will equip you with the knowledge to identify and manage impetigo. Plus, we’ll reveal a groundbreaking online dermatology platform that provides timely consultations, bringing expert advice right to your fingertips. Prepare to discover the key to radiant, impetigo-free skin and embark on a journey to healthier living!
What is Impetigo?
Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection caused largely by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It is most common in young children, particularly those in close touch with one another, such as in schools or daycare settings. It can, however, afflict adults, particularly those with weakened immune systems or specific skin diseases.
Types of Impetigo
Impetigo, a common bacterial skin infection, manifests in two primary forms, each with distinct characteristics and symptoms. Recognizing these types is essential for accurate diagnosis and the appropriate course of treatment:
Non-bullous Impetigo:
Below, you will find information about the characteristics of Non-bullous Impetigo.
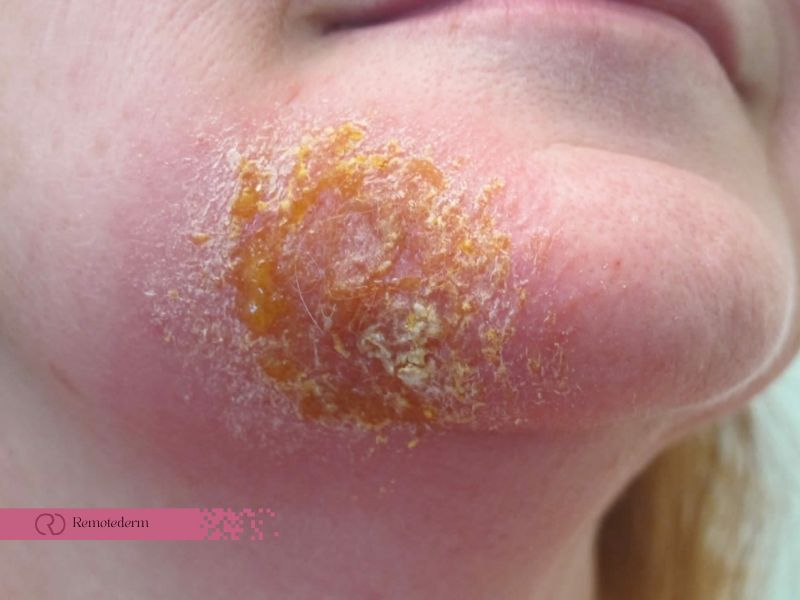
- Non-bullous impetigo, also known as impetigo contagiosa, is the most prevalent form, accounting for approximately 70% of all impetigo cases.
- The infection typically begins as small red papules or lesions, which progress into fluid-filled blisters.
- As the blisters rupture, they leave behind characteristic honey-colored crusts, which are often itchy and may cause discomfort.
- This type of impetigo commonly occurs on the face, especially around the nose and mouth. However, it can also affect other parts of the body, particularly where the skin has been injured or irritated.
Bullous Impetigo:
Read below to learn about the characteristics of Bullous Impetigo.
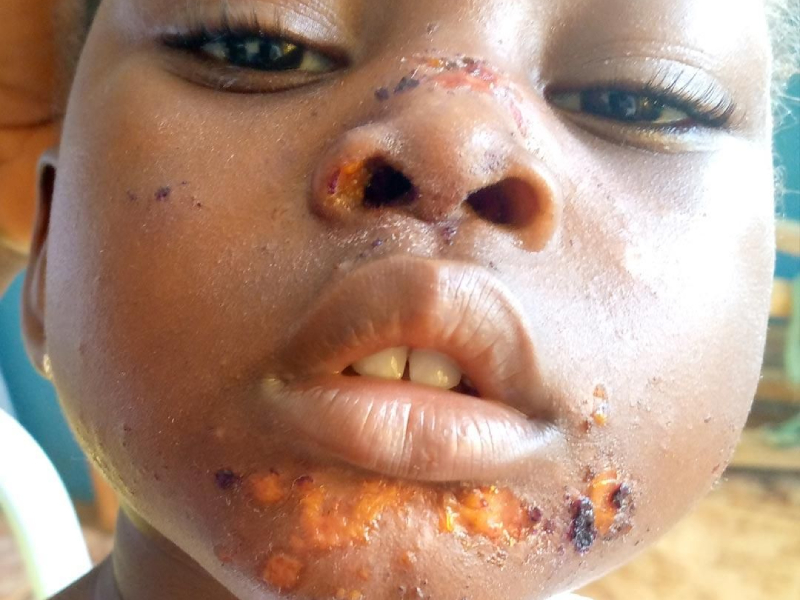
- Bullous impetigo is less common but more severe than non-bullous impetigo.
- It is characterized by the formation of large, clear, and fluid-filled blisters, which do not rupture easily.
- The skin around the blisters may appear red and inflamed, and the blisters themselves are often painless but can be itchy.
- Bullous impetigo is frequently observed on the trunk, buttocks, and diaper area in infants and young children.
- If left untreated, this type of impetigo can lead to more severe complications, such as deeper skin infections.
Both types of impetigo are highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects. In crowded settings like schools or daycare centers, where close contact is common, the risk of transmission is heightened. Thus, maintaining proper hygiene and taking necessary precautions are essential to prevent the spread of impetigo.
A correct diagnosis by a healthcare professional, preferably a dermatologist, is vital for effective treatment and to avoid potential complications. Early identification and prompt initiation of appropriate therapies, such as topical or oral antibiotics, can expedite recovery and reduce the risk of further transmission.
Symptoms of Impetigo
Impetigo presents with characteristic symptoms that can help distinguish it from other skin conditions. Recognizing these signs is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment:
- Red Sores or Blisters: Impetigo typically begins with small red sores or blisters on the skin. These lesions may be itchy or painful, causing discomfort to the affected individual.
- Fluid-Filled and Itchy Blisters: As the infection progresses, the red sores develop into fluid-filled blisters. These blisters can be clear or cloudy and may burst, leading to the formation of honey-colored crusts on the skin surface.
- Honey-Colored Crusts: The presence of honey-colored crusts on the skin is a defining feature of impetigo. These crusts result from the drying of the fluid in the blisters and are often a key indicator of the infection.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: In some cases, individuals with impetigo may experience swollen lymph nodes in the area where the infection is present. This can be a sign that the body is actively fighting the bacterial infection.
- Mild Fever: While not always present, some individuals with impetigo may develop a mild fever, especially if the infection is severe or has spread to a larger area of the body.
It is essential to be aware of these symptoms and seek medical attention if you or your child exhibit any signs of impetigo. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can prevent the spread of the infection and ensure a quicker recovery process. Consulting a healthcare professional, preferably a dermatologist, is recommended to receive the appropriate care and management for impetigo symptoms.
Causes of Impetigo
Impetigo is primarily caused by two types of bacteria:
- Staphylococcus aureus and,
- Streptococcus pyogene
These bacteria commonly reside on the skin’s surface and can enter the body through cuts, insect bites, or other skin injuries, initiating the infection.
Several factors can increase the risk of contracting impetigo, including poor hygiene practices, living in crowded environments, and having skin conditions that create openings for bacteria to enter. Children are particularly susceptible to impetigo due to their close contact in schools and daycare settings.
Direct contact with an infected person or contact with contaminated materials, such as towels, clothing, or toys, is an easy way for the virus to spread. Individuals with compromised immune systems are also more likely to develop impetigo.
Preventing impetigo involves maintaining good hygiene, promptly treating skin injuries, and avoiding contact with infected individuals or their belongings. By understanding the causes and taking appropriate preventive measures, the likelihood of contracting impetigo can be significantly reduced.
Treatment Options
As a dermatologist’s guide, it is essential to discuss the treatment methods available for impetigo.
1. Topical Antibiotics
For mild cases of impetigo, topical antibiotics in the form of creams or ointments are usually prescribed. These antibiotics help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection and promote healing of the skin sores. It is crucial to apply the medication as directed by the healthcare provider and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
2. Oral Antibiotics
In more severe cases or when topical treatments prove ineffective, oral antibiotics may be necessary. Oral antibiotics work from within the body to combat the bacterial infection and reduce the risk of spreading the disease to others. It is vital to take the prescribed oral antibiotics as directed and complete the full course of treatment to prevent antibiotic resistance.
3. Proper Hygiene
Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial in preventing the spread of impetigo. Regularly washing hands with soap and water, especially after touching infected areas or applying medication, can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Keeping the affected areas clean and dry is also essential for promoting healing and preventing the infection from spreading to other parts of the body or to other individuals.
4. Warm Compress
Using a warm compress on the affected areas can help soothe discomfort and aid in the healing process. Gently apply a warm, damp cloth to the affected skin for a few minutes several times a day to reduce pain and inflammation.
5. Avoiding Scratching
It is crucial to avoid scratching the impetigo sores, as this can worsen the infection and lead to the spread of bacteria to other parts of the body. Trimming nails and using distraction techniques for children can help prevent scratching and further complications.
Prevention
Preventing impetigo involves adopting good hygiene practices and taking necessary precautions, especially for individuals who have a higher risk of contracting the infection, such as children and those with weakened immune systems.
1. Regular Handwashing
Frequent handwashing with soap and water can significantly reduce the risk of impetigo transmission. Encourage children to wash their hands regularly, especially after playing with others or touching potentially contaminated objects.
2. Keeping Sores Covered
If you or your child has impetigo, keeping the sores covered with a clean bandage can help prevent the spread of bacteria to others. Change the bandages regularly and dispose of them properly.
3. Avoiding Close Contact
If someone in your household has impetigo, try to minimize close physical contact until the infection is completely healed. Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, with an infected individual.
4. Disinfecting Objects
Regularly disinfecting commonly used objects and surfaces, such as toys, doorknobs, and bathroom fixtures, can help prevent the spread of bacteria. Use a disinfectant that is antibacterial and antiviral.
When to See a Doctor
In most cases, impetigo can be treated effectively with topical or oral antibiotics. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if:
- The infection worsens despite using prescribed medications.
- The affected person develops a fever or experiences severe pain.
- The lymph nodes become swollen and tender.
A healthcare provider, typically a dermatologist, can accurately diagnose impetigo and recommend the most suitable treatment plan based on the individual’s age, medical history, and the severity of the infection. However, for individuals seeking faster access to dermatological consultations, especially those residing in remote areas or facing long waits for in-person appointments, RemoteDerm offers a convenient solution.
RemoteDerm is an innovative online dermatology platform that provides expert consultation for impetigo treatment online within 12 hours to patients across Canada. Through RemoteDerm, individuals can upload images of their skin condition securely and confidentially, allowing dermatologists to assess the symptoms remotely. This service eliminates the need for physical visits to dermatology clinics, which can be challenging for those living in rural or underserved regions.

The timely diagnosis provided by RemoteDerm’s experienced dermatologists allows for early intervention and the prompt initiation of treatment. This not only accelerates the healing process but also helps prevent the further spread of impetigo or potential complications associated with delayed treatment.
Impetigo Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding impetigo, its causes, symptoms, and treatment methods is crucial for effectively managing this common bacterial skin infection. Whether you’re a concerned parent or an individual seeking to protect your skin health, this comprehensive guide has equipped you with valuable knowledge to identify, prevent, and treat impetigo.
Remember, prompt and accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional, preferably a dermatologist, is essential for successful treatment and to prevent potential complications. Timely initiation of appropriate therapies, such as topical or oral antibiotics, can expedite recovery and reduce the risk of further transmission.
Maintaining proper hygiene practices, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and promptly treating skin injuries can significantly lower the risk of contracting impetigo. Regular handwashing, keeping sores covered, and disinfecting commonly used objects are simple yet effective preventive measures.
FAQs
- How does impetigo spread?
Impetigo spreads through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects.
- Can impetigo be treated with topical antibiotics?
Yes, mild cases of impetigo can be treated with topical antibiotics in the form of creams or ointments.
- Can impetigo lead to complications if left untreated?
Yes, if left untreated, impetigo can lead to a variety of complications that can significantly impact the affected individual’s health and well-being.
- How can I ensure a quicker recovery from impetigo?
Early diagnosis, prompt treatment, and adherence to prescribed medications can expedite recovery.