Are you experiencing red, itchy bumps around your hair follicles? You may be suffering from folliculitis, a common skin infection that affects people of all ages and skin types. Folliculitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The condition can be uncomfortable and unsightly, but fortunately, there are several treatment options available. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for folliculitis. Whether you have been diagnosed with folliculitis or are simply interested in learning more about the condition, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the information you need.
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed. Hair follicles are tiny pockets in the skin that contain hair roots and oil glands. When these follicles become infected, they can become red, swollen, and tender to the touch. Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where there are hair follicles, including the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, arms, and legs.
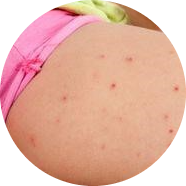
There are several different types of folliculitis, each with its own unique causes and symptoms:
- Bacterial folliculitis is one of the most common types and is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. This type of folliculitis often affects the beard and neck area in men and can be caused by shaving, ingrown hairs, or skin injuries.
- Fungal folliculitis is another type that is caused by fungi such as yeast or mold. This type of folliculitis is more common in warm, humid climates and can be caused by wearing tight clothing or excessive sweating.
- Viral folliculitis is a rare type that is caused by a viral infection such as herpes or shingles.
The causes of folliculitis can vary depending on the type. Bacterial folliculitis is typically caused by bacteria entering the hair follicle, while fungal folliculitis can be caused by excessive sweating or living in a humid environment.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
Symptoms of folliculitis can vary depending on the severity and type of the condition. In most cases, folliculitis presents as small red bumps or pus-filled pimples around hair follicles. These bumps may be itchy, tender, or painful to the touch. Here are some of the common symptoms of folliculitis:
- Small red bumps: These are the most common symptom of folliculitis. They may appear as small red or white bumps around hair follicles.
- Itching: Folliculitis can cause intense itching around the affected area. This can be a result of inflammation and irritation of the skin.
- Pain or tenderness: In some cases, folliculitis can cause pain or tenderness around the affected hair follicles. This can make it uncomfortable to wear tight clothing or touch the area.
- Pus-filled blisters: In severe cases of folliculitis, pus-filled blisters may appear around hair follicles. These may rupture and ooze pus, which can lead to further infection.
- Scarring: If folliculitis is left untreated, it can lead to scarring and permanent hair loss around the affected area. This is more likely to occur in cases of chronic folliculitis.
- Spreading: Folliculitis can spread to other areas of the body if left untreated or if the infection becomes severe. This is more likely to occur in cases of bacterial folliculitis.
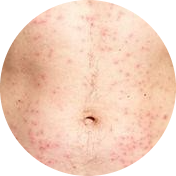
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention. Your dermatologist can diagnose the type and severity of folliculitis and recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of Folliculitis
The treatment of folliculitis depends on its severity, underlying cause, and the affected area. Here are some common treatment options:
Self-care and home remedies
In mild cases of folliculitis, self-care, and home remedies can effectively reduce symptoms and promote healing. Here are some self-care tips for managing folliculitis at home:

- Avoid shaving the affected area until the inflammation subsides.
- Apply warm compresses to the affected area to reduce pain and swelling.
- Keep the affected area clean and dry.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing or clothing made of synthetic materials that can irritate the skin.
- Use a mild antibacterial soap or shampoo to cleanse the affected area.
- Apply over-the-counter topical creams or ointments, such as hydrocortisone, to reduce inflammation and itching.
Medical treatments
In more severe cases of folliculitis, medical treatments may be necessary to manage the symptoms and prevent complications. Here are some medical treatment options for folliculitis:
- Topical antibiotics: These are medications that are applied directly to the affected area to kill bacteria or fungi. Common topical antibiotics used to treat folliculitis include mupirocin, clindamycin, and neomycin.
- Oral antibiotics: These are medications that are taken orally to kill bacteria or fungi. Oral antibiotics are usually prescribed for more severe or recurrent cases of folliculitis. Common oral antibiotics used to treat folliculitis include cephalexin, doxycycline, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
- Antifungal medications: These are medications that are used to treat fungal infections that cause folliculitis. Common antifungal medications used to treat folliculitis include terbinafine and fluconazole.
- Corticosteroids: These are medications that are used to reduce inflammation and itching associated with folliculitis. Corticosteroids are usually prescribed for severe cases of folliculitis that do not respond to other treatments.
Diagnosis of Folliculitis
Before any treatment can begin, an accurate diagnosis must be made. Here are some of the diagnostic procedures used to diagnose folliculitis:

- Physical examination: The first step in diagnosing folliculitis is a physical examination of the affected area. The doctor will look at the skin and hair follicles to determine the extent and severity of the condition. They will also ask about symptoms, such as itching, redness, and tenderness.
- Medical history: The doctor may ask about the patient’s medical history, including any past skin conditions, recent illnesses, and medications are taken. This information can help the doctor determine the cause of the folliculitis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- Skin culture: A skin culture involves taking a sample of the affected skin and testing it for bacterial or fungal infection. This can help the doctor determine the specific type of infection causing the folliculitis and prescribe the most effective medication.
- Skin biopsy: In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to diagnose folliculitis. This involves taking a small sample of skin tissue for laboratory analysis. A skin biopsy can help determine the underlying cause of the folliculitis, such as a skin condition or autoimmune disorder.
- Blood tests: Blood tests are not typically used to diagnose folliculitis, but they may be ordered if the doctor suspects an underlying condition, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system.
- Dermoscopy: Dermoscopy is a non-invasive imaging technique that can be used to examine the skin and hair follicles in greater detail. This can help the doctor identify any subtle changes in the skin that may indicate an underlying condition or infection.
- X-rays: X-rays are not typically used to diagnose folliculitis, but they may be ordered if the doctor suspects an underlying condition, such as a bone infection.
In conclusion, an accurate diagnosis of folliculitis is essential to developing an effective treatment plan.
Folliculitis Prevention
Preventing folliculitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of developing the condition. Here are some prevention tips for folliculitis:
- Avoid shaving the affected area until the inflammation subsides.
- Keep the affected area clean and dry.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing or clothing made of synthetic materials that can irritate the skin.
- Use a clean razor or electric shaver when shaving.
- Avoid sharing towels, razors, or other personal items that can spread bacteria or fungi.
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly and taking regular showers or baths.
- Treat skin injuries promptly to prevent infection.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, folliculitis is a common skin condition that can cause discomfort and unsightly bumps around hair follicles. The condition can be caused by bacteria, fungi, and viruses, and can occur anywhere on the body with hair follicles. Symptoms of folliculitis include small red bumps, itching, pain or tenderness, pus-filled blisters, scarring, and spreading. Treatment options include self-care and home remedies, as well as medical treatments such as antibiotics, antifungal medications, and corticosteroids.

Patients can benefit from online dermatologist services like Remotederm from the comfort of their homes by receiving a quick and accurate diagnosis from a board-certified dermatologist. You can access treatment options and recommendations for managing symptoms or preventing complications. This can save time and money, and also provide peace of mind knowing that they are receiving professional advice from the comfort of their home.
Additionally, online dermatology consultation services can often provide faster and more efficient care. Instead of waiting weeks or even months for an in-person appointment, patients can often receive a diagnosis and treatment plan within a matter of days or even hours. This can be especially important for patients with acute or severe cases of folliculitis, as early treatment can help prevent complications and promote faster healing.
FAQs
1. Is folliculitis contagious?
Folliculitis is generally not contagious, but it can be spread through contact with infected items like towels, clothing, and personal hygiene products.
2. Can folliculitis go away on its own?
Mild cases of folliculitis can often go away on their own without treatment. However, more severe cases may require medical intervention to prevent complications.
3. How is folliculitis diagnosed?
Folliculitis can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare provider. In some cases, a skin culture or biopsy may be necessary to determine the specific type of folliculitis.
4. How long does it take for folliculitis to heal?
The healing time for folliculitis can vary depending on the severity and type of the condition. Mild cases may heal within a few days, while more severe cases may take several weeks or longer to resolve.
5. Can folliculitis cause permanent hair loss?
In some cases, folliculitis can cause scarring and permanent hair loss around the affected area. This is more likely to occur in cases of chronic folliculitis that are left untreated.
