Scalp conditions can come in various forms and can cause severe symptoms. Most scalp conditions are not contagious and some are inherited, while others can be caused by malnutrition or infection. Accurate diagnosis and treatment depend on the specific cause of the scalp condition. Common symptoms of scalp conditions include itching, inflammation, and skin flaking. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist, for a thorough examination and proper diagnosis in order to receive appropriate treatment.
This article will discuss common scalp conditions and treatment options.
Different types of Scalp conditions
Scalp Eczema (Dermatitis)
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common form of eczema that can affect the scalp and hairline. It can occur in babies, children, and adults and is characterized by red, scaly skin with dandruff and a rash that may vary in severity. The rash may also appear on other parts of the body, such as the eyebrows, eyelids, sides of the nose, and the creases of the knees and elbows.
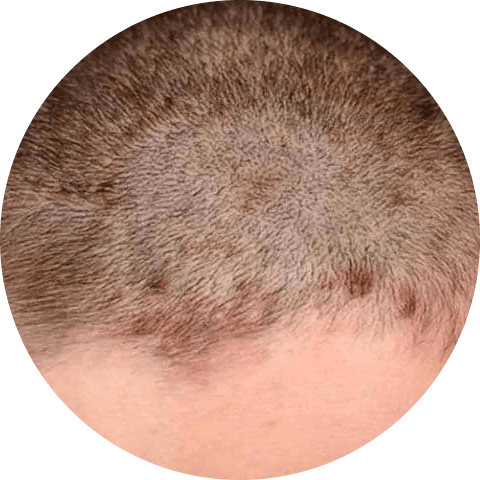

Does scalp Eczema lead to hair loss?
While seborrheic dermatitis or scalp eczema itself may not directly cause hair loss, the act of scratching and itching the scalp can damage the scalp and hair follicles. This can lead to brittle hair, which can cause some hair loss.
| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation of the hair follicles. It is often caused by a bacterial infection and may initially appear as small pimples around the hair follicles. Mild cases of folliculitis can typically be treated with self-care measures and will heal without scarring within a few days. However, more severe or recurrent infections may require prescription medication. If left untreated, severe infections can result in permanent hair loss and scarring.
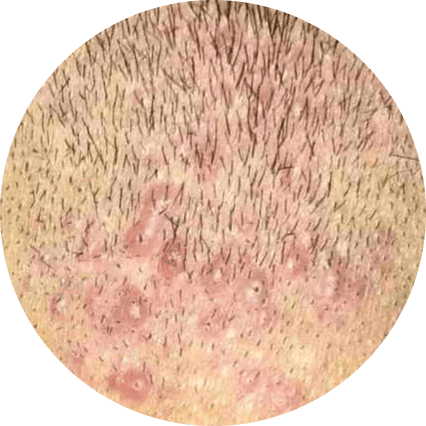
| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
Is folliculitis a sexually transmitted disease?
Folliculitis is not a sexually transmitted infection, but it can be transmitted through close skin contact in some cases. The herpes simplex virus, on the other hand, is spread through sexual contact. This virus can cause folliculitis in rare cases.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is a common hair loss condition that affects both men and women. In fact, by the age of 50, the condition affects 30% to 50% of men. Androgenetic alopecia is also referred to as “male-pattern baldness.” The pattern of hair loss in women differs; thin hair is distributed over the entire head, and the hairline does not usually recede as it does in men.

| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
Is it possible to regrow hair after androgenetic alopecia?
If you have androgenetic alopecia, you may experience hair regrowth, but the rate of regrowth varies from person to person. Although androgenetic alopecia cannot be prevented, there are numerous hair loss treatments available to slow the process or restore hair permanently.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune skin disease that causes hair loss on the scalp, face, and other body parts. The body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing them to shrink and slow hair growth. There could be a cycle of hair loss that involves unpredictable regrowth and loss.
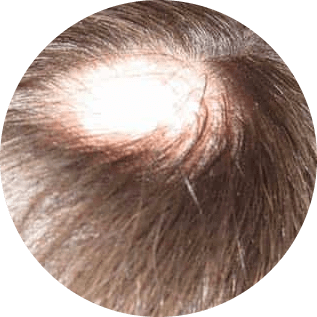
The three varieties of alopecia areata are as follows:
- Alopecia areata: Small, coin-sized patches of hair loss appear on the scalp, around the beard area, on the eyelashes, in the armpits, and in the brows.
- Alopecia totalis: This results in complete hair loss on the scalp.
- Alopecia Universalis: This results in total hair loss throughout the body and scalp.
| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
How is alopecia areata scalp condition treated?
Although there is no cure for alopecia areata, it can be treated and hair can regrow. There are several treatment options available for alopecia areata, including the use of corticosteroids, which are anti-inflammatory drugs used to treat autoimmune diseases. Other treatment options may also be used to manage alopecia areata.
Head Lice
Head lice are tiny insects that can cause itching and small red bumps on the neck, scalp, and shoulders. They are not visible to the naked eye, but their eggs, called nits, can be seen as small, round or oval-shaped globs of hair attached to the hair near the scalp. Nits may be mistaken for dandruff, but they are more difficult to remove. They can cause discomfort and may require treatment to eliminate the lice infestation.
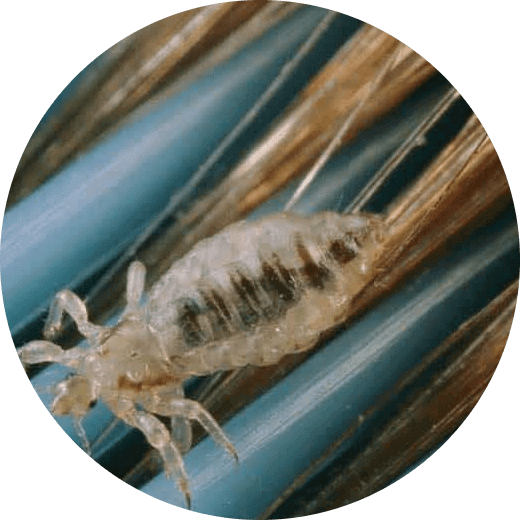

| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
How long do head lice last?
Head lice will be completely eradicated after two to three weeks of effective treatment. The duration is determined by the number of lice that have made a home in your hair. To get rid of lice quickly, make sure you follow the directions on your medicated shampoo, lotion, or cream. If left untreated, lice can live on your head for up to 30 days or longer.
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the development of itchy, small patches of hair loss on the scalp. It is also known as scarring alopecia, and is an inflammatory skin condition.
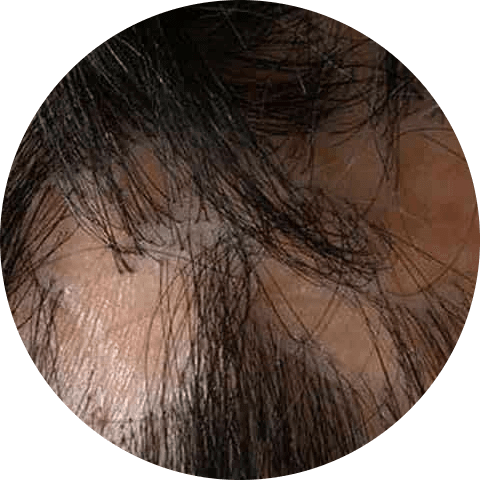
Lichen planus is a condition that can often be managed at home for mild cases, but severe pain or itching may require prescription medication. It is important to note that lichen planus is not contagious. If you are experiencing severe symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
Is Lichen Planus contagious?
Lichen planus cannot be transmitted from one person to another through skin-to-skin contact or unprotected sexual activity. It is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person. It is important to note that lichen planus is a condition that affects the skin and is not caused by an infectious agent.
After Lichen Planus, can hair grow again?
Lichen planopilaris is a condition that cannot be cured, but it can be managed with treatment. Some approaches used to treat this condition are similar to those used for alopecia areata, such as the use of corticosteroids. These medications can help to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs.
Tinea Capitis (Ringworm)
Ringworm is a fungal infection that affects the outer layer of the scalp. It is characterized by the development of a rash with circular patches and raised, red edges. The rash tends to spread from the outside of the circle, leaving the inside unaffected, which gives it a ring-shaped appearance.
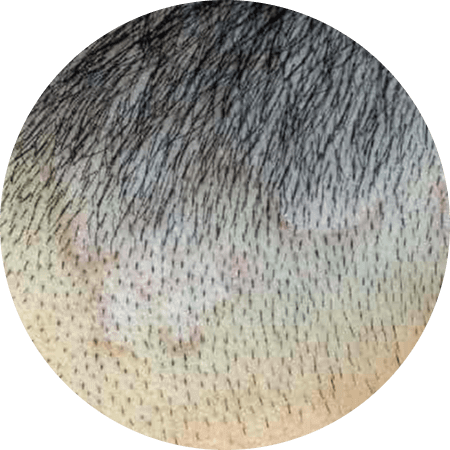
Unlike many other scalp conditions, ringworm is contagious. It can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or by sharing personal items such as hats, combs, brushes, clothing, or towels. It is important to practice good hygiene and avoid sharing items to prevent the spread of this infection.
If you like to get information about skin cancer you can click on the link and read the article.
| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a genetic autoimmune disorder that causes long-term inflammation and periods of remission and relapse. It affects the scalp in about half of all cases, and can range from mild, almost undetectable symptoms to severe, long-lasting sores that are thick and crusted. Scalp psoriasis can cause itching that can disrupt sleep and daily activities, and frequent scratching can lead to skin infections and hair loss. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan to manage the symptoms of this condition.
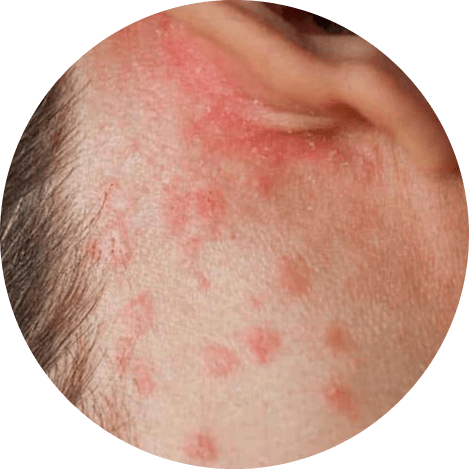
| Symptoms |
|
| Underlying Causes |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Prevention |
|
What vitamin deficiency causes scalp psoriasis?
There is a link between psoriasis and vitamin D deficiency. Although a deficiency is not believed to be the direct cause of psoriasis, it may weaken the body’s ability to maintain healthy skin, which could increase the frequency of flare-ups. Adequate intake of vitamin D may help to improve symptoms of psoriasis. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate levels of vitamin D for your individual needs.
Diagnosis of scalp conditions
During a history and physical examination, many scalp skin conditions can be diagnosed. A diagnostician can examine the scalp and gather information about the patient’s history of symptoms to make a diagnosis. However, the symptoms of many scalp disorders can overlap, and diagnostic tests may be necessary to differentiate between different possibilities. In some cases, a dermatologist may be consulted to assist with the diagnosis. Factors that may be considered in the diagnosis of a scalp condition include:
- The appearance and location of any lesions or rashes
- The patient’s medical history
- Results of any diagnostic tests
- The presence of any other symptoms. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to accurately diagnose and treat any scalp condition.
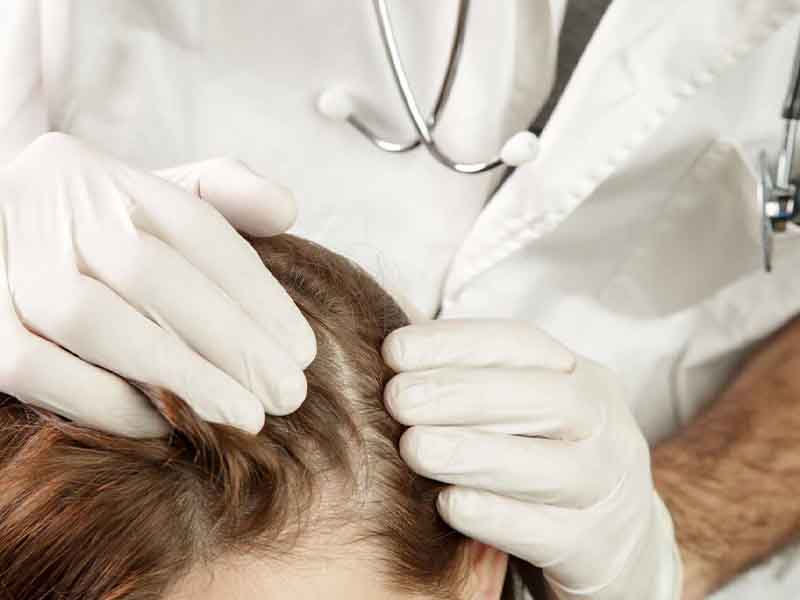
To accurately diagnose a scalp condition, a healthcare provider may conduct a thorough physical examination to evaluate visible symptoms on the scalp skin. They may also ask about the patient’s family medical history to determine if there are any hereditary scalp conditions, such as psoriasis, present. Other diagnostic tests that may be used to assess scalp conditions include:
- A pull test to measure the extent of hair loss in people with alopecia
- A scalp biopsy, in which a small sample of scalp tissue is removed and examined under a microscope to identify the type of scalp condition or the cause of hair loss
- Cultures, in which a sample of tissue is examined under a microscope to check for a specific type of infection. These tests can help the healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the scalp condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
You can get information about online dermatology consultation by click on the link.
Final Thoughts and outlook for patients with scalp conditions
There are various factors that can cause scalp skin conditions, and the appropriate treatment approach may depend on the specific condition. Some conditions may be managed with self-care strategies, while others may require medical treatment. If a certain treatment is not effectively reducing the severity of the condition, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Many people with scalp conditions can maintain a positive outlook, as medications that slow hair loss or promote hair regrowth can be somewhat effective. Additionally, research on the treatment of various scalp skin conditions is ongoing. Infection-related scalp conditions can often be treated and eliminated, while some other scalp conditions may not be curable but can still be managed with treatment to slow the progression of symptoms. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs.

6 comments
Great article, thank you! Can scalp eczema be caused by stress or anxiety?
Yes, scalp eczema (dermatitis) can be caused or worsened by stress or anxiety. Emotional stress can trigger or exacerbate many skin conditions, including scalp eczema. In fact, stress is often cited as a major contributing factor in eczema flare-ups.
I didn’t know that folliculitis could be caused by using hair products, how can I avoid this?
Yes, folliculitis can be caused by using hair products that irritate the hair follicles, such as gels, pomades, and hairsprays. To avoid folliculitis, it’s important to avoid using these types of products if possible. If you do use hair products, make sure to wash your hair and scalp thoroughly afterwards to remove any residue. You may also want to try using products that are specifically designed for sensitive skin.
I recently discovered that I have lichen planus on my scalp. I’m wondering if there are any lifestyle changes I can make to help alleviate the symptoms?
Thank you for your comment. While there are no proven lifestyle changes that can cure lichen planus, some people find relief from avoiding certain triggers such as stress, harsh hair products, or sun exposure. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet and managing stress levels may help alleviate symptoms.